2026-01-21 マサチューセッツ大学アマースト校
<関連情報>
- https://www.umass.edu/news/article/new-umass-amherst-led-study-shows-analog-hardware-may-solve-internet-things-speedbumps
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s44460-025-00013-z
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-025-01555-3
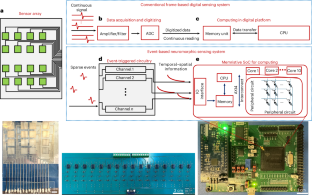
柔軟な触覚センサーとメモリスティブシステムを搭載したチップ上のイベントベースのニューロモルフィックセンシングシステム Event-based neuromorphic sensing system with flexible haptic sensors and a memristive system on a chip
Wuyu Zhao,Yi Huang,Amit Tewari,Alireza Jaberi Rad,Andrew Zhang,Ning Ge,J. Joshua Yang,Miao Hu,Sayani Majumdar & Qiangfei Xia
Nature Sensers Published:19 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s44460-025-00013-z
Abstract
The rapid growth of Internet of Things applications has substantially increased the number of connected sensors and data volume, yet conventional digital conversion and transmission systems impose high energy and latency costs. Here we develop a neuromorphic sensing system integrating a flexible piezoelectric haptic sensor array, event-triggered preprocessing circuitry and a memristive system on a chip. The circuitry transforms transient voltage spikes from sensor pixels into decaying voltage waveforms, generating a time surface for event-based analogue in-memory computing within the chip. Our system achieves 87%–92% recognition accuracy for patterns written on the sensor array and reduces the energy-delay product during inference compared with conventional digital platforms. These results highlight the potential of the memristive system on a chip for energy-efficient, low-latency edge processing of analogue sensor data, advancing intelligent sensing technologies.
高速ピクセル内コンピューティングのためのメモリスティブセルラーニューラルネットワーク Memristive cellular neural networks for fast in-pixel computing
Vignesh Ravichandran,Yi Huang,Bryce Flannery,Tergel Molom-Ochir,Tina Maurer,Shiva Asapu,Ali Abdel-Maksoud,Nia Heermance,Remy Yoo,Joshua Tackie,Wuyu Zhao,Yunzhi Ling,Alex Guo,J. Joshua Yang & Qiangfei Xia
Nature Electronics Published:19 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-025-01555-3
Abstract
Cellular neural networks, inspired in part by the biological retina, offer a potential route to massively parallel analogue computing. However, the hardware implementation of such systems remains challenging. Here we report memristor-based cellular neural networks for image and video processing applications. We develop a Python-based digital twin for network simulations and as a graphical user interface for controlling the fabricated hardware. Simulations using the digital twin illustrate the network’s capabilities in image processing and in solving partial differential equations. We build hardware through the tape-out of a transistor-based network and the fabrication of a circuit board with multilevel non-volatile memristors as the synapses. We show that the hardware can be used to run image processing tasks including edge and horizontal line detection.