2025-09-09 自然科学研究機構
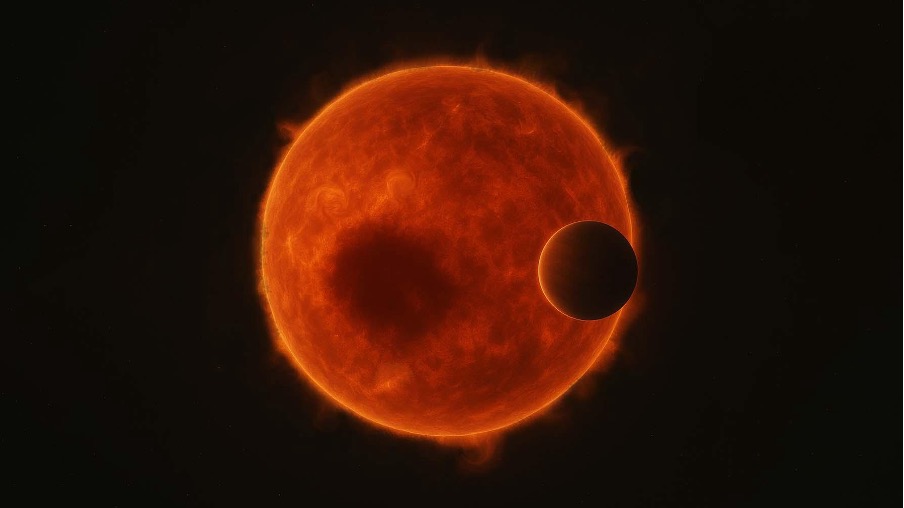 TOI-3884系の想像図。大きな黒点を持つ赤色矮星TOI-3884の前をスーパーネプチューンTOI-3884bが横切っている様子。画像クレジット: 森万由子,アストロバイオロジーセンター(生成AIおよび画像編集ツールを使用)
TOI-3884系の想像図。大きな黒点を持つ赤色矮星TOI-3884の前をスーパーネプチューンTOI-3884bが横切っている様子。画像クレジット: 森万由子,アストロバイオロジーセンター(生成AIおよび画像編集ツールを使用)
<関連情報>
- https://www.abc-nins.jp/a-planet-crossing-starspots-reveals-the-detailed-architecture-of-the-toi-3884-system/
- https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-3881/ade2df
多波長・多時期光度測定によるトイ-3884星の交差スポット系:精緻化された系幾何学とスポット特性 Multiband, Multiepoch Photometry of the Spot-crossing System TOI-3884: Refined System Geometry and Spot Properties
Mayuko Mori, Akihiko Fukui, Teruyuki Hirano, Norio Narita, John H. Livingston, Khalid Barkaoui, Karen A. Collins, Jerome P. de Leon, Kai Ikuta, Yugo Kawai,…
The Astronomical Journal Published: 2025 September 8
DOI: 10.3847/1538-3881/ade2df
Abstract
Spot-crossing transits offer a unique opportunity to probe spot properties such as temperature, size, and surface distribution. TOI-3884 is a rare system in which spot-crossing features are persistently observed during every transit. This is due to its unusual configuration: a nearly polar-orbit super-Neptune transits a pole-on mid-M dwarf, repeatedly crossing a polar spot. However, previous studies have reported discrepant values in key system parameters, such as stellar inclination and obliquity. To address this, we conducted multiband, multiepoch transit observations of TOI-3884 b using the MuSCAT instrument series, along with photometric monitoring with the Las Cumbres Observatory 1 m telescopes/Sinistro. We detected time-dependent variations in the spot-crossing signals, indicating that the spot is not exactly on the pole. From the monitoring data, we measured a stellar rotation period of 11. 043+0.045-0.053 days with a modulation amplitude of ∼5% in the r band, consistent with the time variability in the spot-crossing features. Our analysis reconciles previous discrepancies and improves the constraints on the parameters of the system geometry ( i★= 139.9+1.2-2.0 deg and λ=41.0+3.7-9.0 deg) and those of the spot properties (spot radius of 0.425+0.018-0.011R★ and a spot–photosphere temperature difference of 200+11-9 K). These results provide a critical context for interpreting upcoming transmission spectroscopy of TOI-3884 b, as well as yielding new insights into the magnetic activity and spin–orbit geometry of M dwarfs.