2025-04-30 中国科学院(CAS)
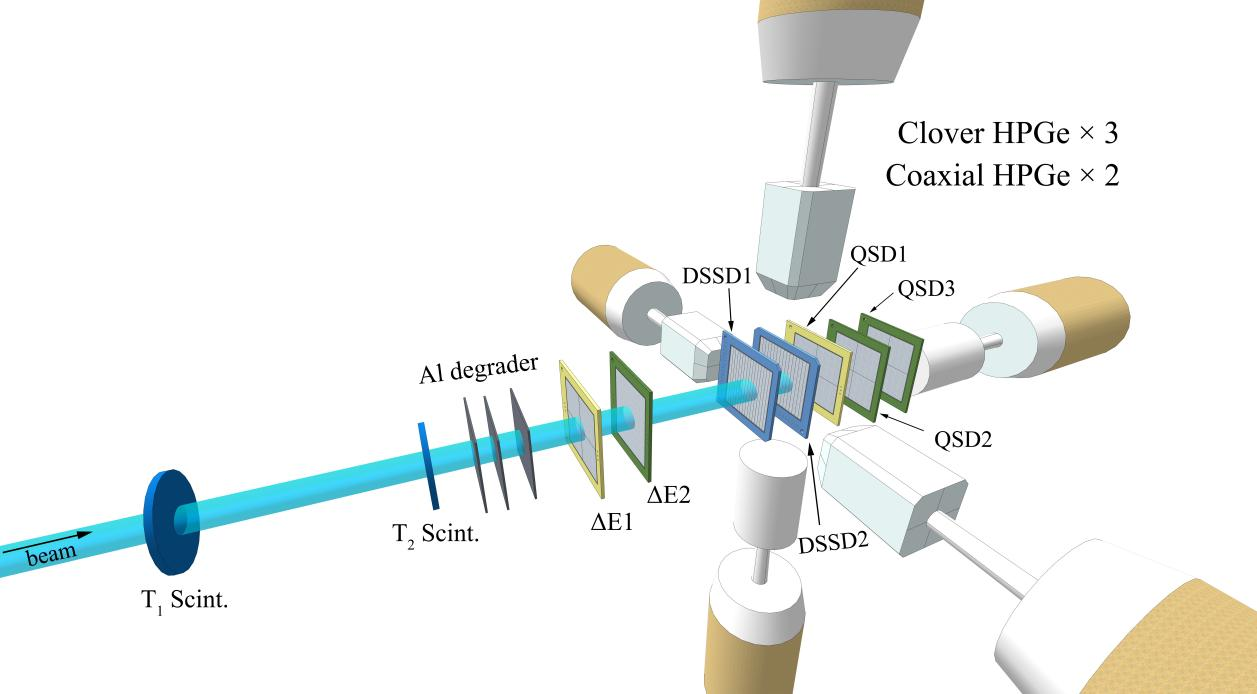 Figure 1. Schematic layout of the digital detector array (Image from IMP)
Figure 1. Schematic layout of the digital detector array (Image from IMP)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/phys/202504/t20250430_1042492.shtml
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s41365-025-01667-7
荷電粒子崩壊研究のためのデジタルデータ収集システムを備えた検出器アレイ Detector array with digital data acquisition system for charged-particle decay studies
Hao Jian,Xin-Xing Xu,Kai-Long Wang,Jia-Jian Liu,Chao-Yi Fu,Peng-Jie Li,Yan-Yun Yang,Guang-Xin Zhang,Kang Wang,Fang-Fang Duan,Long-Hui Ru,Guang-Shun Li,Bing Ding,Yun-Hua Qiang,Cen-Xi Yuan,Jun-Bing Ma,Shi-Wei Xu,Yu-Feng Gao,Rui Fan,Fan-Chao Dai,Si-Xian Zha,Hao-Fan Zhu,Jin-Hai Li,Shu-Lian Qin,… Jenny Lee
Nuclear Science and Techniques Published:12 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-025-01667-7
Abstract
A state-of-the-art detector array with a digital data acquisition system has been developed for charged-particle decay studies, including β-delayed protons, α decay, and direct proton emissions from exotic proton-rich nuclei. The digital data acquisition system enables precise synchronization and processing of complex signals from various detectors, such as plastic scintillators, silicon detectors, and germanium γ detectors. The system’s performance was evaluated using the β decay of 32Ar and its neighboring nuclei, produced via projectile fragmentation at the first Radioactive Ion Beam Line in Lanzhou (RIBLL1). Key measurements, including the half-life, charged-particle spectrum, and γ-ray spectrum, were obtained and compared with previous results for validation. Using the implantation–decay method, the isotopes of interest were implanted into two double-sided silicon strip detectors, where their subsequent decays were measured and correlated with preceding implantations using both position and time information. This detection system has potential for further applications, including the study of β-delayed charged-particle decay and direct proton emissions from even more exotic proton-rich nuclei.