2025-03-04 東京大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/ja/press/10693/
- https://www.jst.go.jp/pr/announce/20250304-2/pdf/20250304-2.pdf
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.20486
LSQCA 限られたスケールのフォールトトレラント量子コンピューティングのためのリソース効率の高いロード/ストアアーキテクチャ LSQCA: Resource-Efficient Load/Store Architecture for Limited-Scale Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computing
Takumi Kobori, Yasunari Suzuki, Yosuke Ueno, Teruo Tanimoto, Synge Todo, Yuuki Tokunaga
arXiv Submitted on 29 Dec 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2412.20486
Abstract
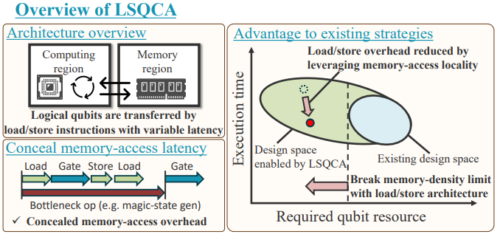
Current fault-tolerant quantum computer (FTQC) architectures utilize several encoding techniques to enable reliable logical operations with restricted qubit connectivity. However, such logical operations demand additional memory overhead to ensure fault tolerance. Since the main obstacle to practical quantum computing is the limited qubit count, our primary mission is to design floorplans that can reduce memory overhead without compromising computational capability. Despite extensive efforts to explore FTQC architectures, even the current state-of-the-art floorplan strategy devotes 50% of memory space to this overhead, not to data storage, to ensure unit-time random access to all logical qubits.
In this paper, we propose an FTQC architecture based on a novel floorplan strategy, Load/Store Quantum Computer Architecture (LSQCA), which can achieve almost 100% memory density. The idea behind our architecture is to separate all memory regions into small computational space called Computational Registers (CR) and space-efficient memory space called Scan-Access Memory (SAM). We define an instruction set for these abstract structures and provide concrete designs named point-SAM and line-SAM architectures. With this design, we can improve the memory density by allowing variable-latency memory access while concealing the latency with other bottlenecks. We also propose optimization techniques to exploit properties of quantum programs observed in our static analysis, such as access locality in memory reference timestamps. Our numerical results indicate that LSQCA successfully leverages this idea. In a resource-restricted situation, a specific benchmark shows that we can achieve about 90% memory density with 5% increase in the execution time compared to a conventional floorplan, which achieves at most 50% memory density for unit-time random access. Our design ensures broad quantum applicability.