2024-02-01 チャルマース工科大学
◆さらに、地域の干ばつや熱波も昼間の気温上昇を促進し、昼夜の気温差の増加は作物や植物、動物、人間の健康に影響を与える可能性がある。これに対処するため、異なる分野での戦略の調整が必要とされている。
<関連情報>
- https://news.cision.com/chalmers/r/increased-temperature-difference-between-day-and-night-can-affect-all-life-on-earth,c3919850
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-43007-6
最近数十年間における陸域の日周下気温の非対称温暖化の逆転 Reversed asymmetric warming of sub-diurnal temperature over land during recent decades
Ziqian Zhong,Bin He,Hans W. Chen,Deliang Chen,Tianjun Zhou,Wenjie Dong,Cunde Xiao,Shang-ping Xie,Xiangzhou Song,Lanlan Guo,Ruiqiang Ding,Lixia Zhang,Ling Huang,Wenping Yuan,Xingming Hao,Duoying Ji & Xiang Zhao
Nature Communications Published:08 November 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43007-6
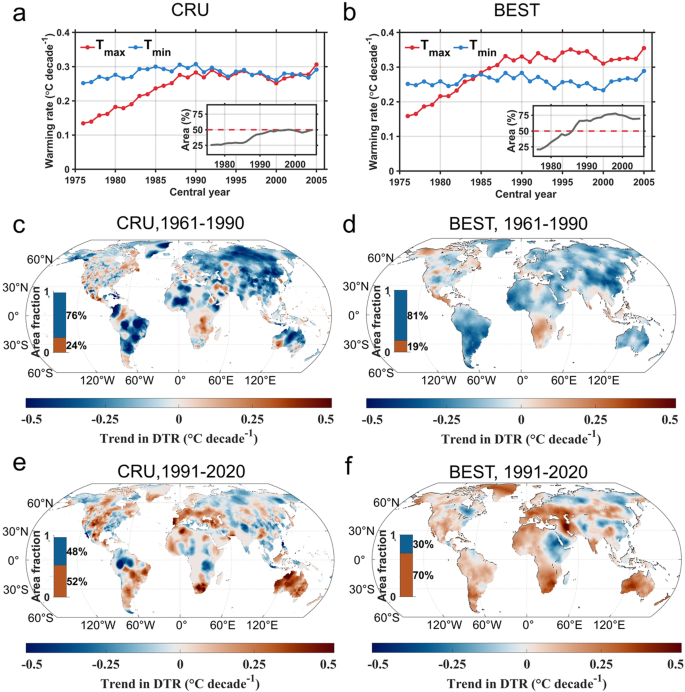
Abstract
In the latter half of the twentieth century, a significant climate phenomenon “diurnal asymmetric warming” emerged, wherein global land surface temperatures increased more rapidly during the night than during the day. However, recent episodes of global brightening and regional droughts and heatwaves have brought notable alterations to this asymmetric warming trend. Here, we re-evaluate sub-diurnal temperature patterns, revealing a substantial increase in the warming rates of daily maximum temperatures (Tmax), while daily minimum temperatures have remained relatively stable. This shift has resulted in a reversal of the diurnal warming trend, expanding the diurnal temperature range over recent decades. The intensified Tmax warming is attributed to a widespread reduction in cloud cover, which has led to increased solar irradiance at the surface. Our findings underscore the urgent need for enhanced scrutiny of recent temperature trends and their implications for the wider earth system.