202303-02 米国国立標準技術研究所(NIST)
研究チームは、この問題を引き起こしているのは水蒸気による酸化であり、それが太陽からの紫外線と組み合わさってアルミニウム酸化物の厚い層を生み出していると結論づけた。
彼らは、水の原因は、宇宙船の機器の温度を制御するために使用されるサーマルブランケットであり、これは今後の衛星の性能を向上させるために、フィルターの露出を制限するためのハードウェアを追加するか、フィルター自体に別の材料を使用することができると考えている。
<関連情報>
- https://www.nist.gov/news-events/news/2023/03/solved-mystery-cloudy-filters
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11207-023-02112-x
太陽観測用宇宙船光学系における紫外線による酸化の危険性 The Hazard of UV-Induced Oxidation to Solar-Viewing Spacecraft Optics
Charles Tarrio,Thomas B. Lucatorto,Robert F. Berg,Dale E. Newbury,Nicholas W. M. Ritchie,Andrew R. Jones & Frank Eparvier
Solar Physics Published:02 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-023-02112-x
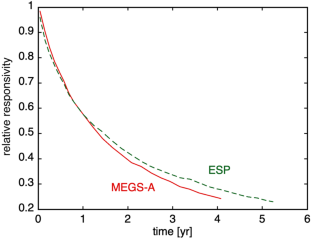
Abstract
The two most prevalent outgassing contaminants on spacecraft are organic molecules and water vapor. Adsorbed organic molecules can degrade a solar-viewing instrument when they are cracked by ultraviolet radiation (UV) and become a light-absorbing layer of carbon. In earlier work, we examined the transmission loss of the extreme-ultraviolet (EUV) aluminum filters used onboard the Solar Dynamics Observatory, and we showed that the degradation was not caused by carbonization. Here, by comparing the losses of the spacecraft filters with the losses induced on similar filters by synchrotron radiation, we demonstrate that the degradation was likely due to oxidation caused by the ultraviolet activation of adsorbed water vapor.


