2026-02-10 中国科学院(CAS)
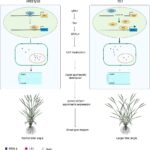
 Dynamic post-translational modification of HtL1/FBA10, a key enzyme in the glycolysis pathway, regulates vernalization-mediated flowering time in wheat. A and B. HtL1 positively regulates flowering time in wheat; C. Cultivars carrying Hap-2 of HtL1 flower later than those carrying Hap-1; D. Declining selection frequency of Hap-2 during Chinese wheat breeding history; E. A working model illustrating how vernalization-induced dynamic post-translational modifications of HtL1 regulate transcription of the flowering promoter VRN1 in wheat. (Imaged by XING Lijing)
Dynamic post-translational modification of HtL1/FBA10, a key enzyme in the glycolysis pathway, regulates vernalization-mediated flowering time in wheat. A and B. HtL1 positively regulates flowering time in wheat; C. Cultivars carrying Hap-2 of HtL1 flower later than those carrying Hap-1; D. Declining selection frequency of Hap-2 during Chinese wheat breeding history; E. A working model illustrating how vernalization-induced dynamic post-translational modifications of HtL1 regulate transcription of the flowering promoter VRN1 in wheat. (Imaged by XING Lijing)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202602/t20260210_1150644.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-67734-0
O -GlcNAcとHtL1/FBA10のリン酸化修飾は、開花のための小麦の春化を制御する O-GlcNAc and phosphorylation modifications on HtL1/FBA10 regulate wheat vernalization for flowering
Pengfang Yang,Yangyang Liu,Qi Dong,Yuting Miao,Jianlong Zhang,Shujuan Xu,Hong Zhao,Yuda Niu,Xueyong Zhang,Yunyuan Xu,Zifeng Guo,Lijing Xing & Kang Chong
Nature Communications Published:27 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-67734-0
Abstract
Vernalization-regulated flowering is vital for wheat yield and geographical distribution, and the diversity of flowering time genes is essential for the breeding of climate-resilient varieties. Sugars have long been recognized in regulating flowering; however, the intrinsic connection between carbohydrate metabolism and vernalization response remains largely unexplored. Here, we identify a fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA) encoding gene, HtL1/FBA10, as a modulator of heading time variation based on a genome-wide association study utilizing wheat core germplasm collections. Evolutionary analysis shows a decrease in the proportion of haplotype-2 of HtL1, which is linked to delayed flowering, in Chinese and American wheat varieties compared to landraces. Vernalization reduces HtL1/FBA10 phosphorylation levels and increases its O-GlcNAcylation, which in turn enhances its enzymatic activity and facilitates VERNALIZATION 1 (VRN1) transcription by regulating histone acetylation at the VRN1 locus. Our findings provide mechanistic insights into the interplay between glucose metabolism and the epigenetic regulation of vernalization in winter wheat.