遷移金属ダイカルコゲナイドヘテロ構造の積層順序を変えると、暗黒励起子が最上層にのみ出現することがわかった。 Dark excitons emerge exclusively at the top layer of bi-layered transition metal dichalcogenide heterostructures when the stacking order of the layers is changed
2023-10-12 韓国基礎科学研究院(IBS)
◆韓国の研究者は、層の順序が「ダークエキシトン」生成に影響を与えることを発見し、これは実用的なデバイス応用において重要です。この研究は、暗いエキシトンを明るいエキシトンに変換できる可能性をもたらし、新しい研究分野を切り拓く重要な進展です。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-41047-6
二層TMDヘテロ構造における順序依存的暗励起子変調 Sequential order dependent dark-exciton modulation in bi-layered TMD heterostructure
Riya Sebait,Roberto Rosati,Seok Joon Yun,Krishna P. Dhakal,Samuel Brem,Chandan Biswas,Alexander Puretzky,Ermin Malic & Young Hee Lee
Nature Communications Published:08 September 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41047-6
Abstract
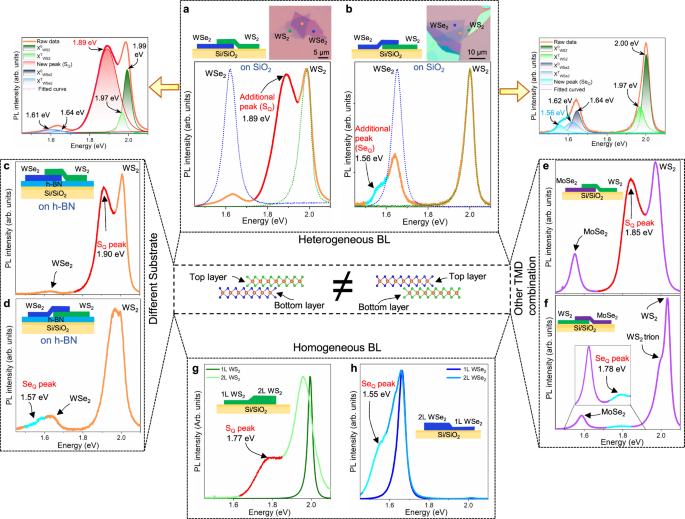
We report the emergence of dark-excitons in transition-metal-dichalcogenide (TMD) heterostructures that strongly rely on the stacking sequence, i.e., momentum-dark K-Q exciton located exclusively at the top layer of the heterostructure. The feature stems from band renormalization and is distinct from those of typical neutral excitons or trions, regardless of materials, substrates, and even homogeneous bilayers, which is further confirmed by scanning tunneling spectroscopy. To understand the unusual stacking sequence, we introduce the excitonic Elliot formula by imposing strain exclusively on the top layer that could be a consequence of the stacking process. We further find that the intensity ratio of Q- to K-excitons in the same layer is inversely proportional to laser power, unlike for conventional K-K excitons. This can be a metric for engineering the intensity of dark K-Q excitons in TMD heterostructures, which could be useful for optical power switches in solar panels.


