量子コンピューターで機械学習モデルを訓練するために多数のパラメーターを使用する場合、多ければ多いほど良い – ある程度までは。 More is better — to a point — when using a large number of parameters to train machine learning models on quantum computers
2023-06-27 ロスアラモス国立研究所(LANL)
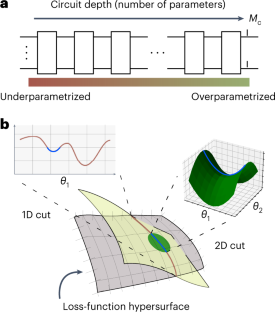
◆研究チームは、量子機械学習モデルがオーバーパラメータ化する臨界点を予測し、パラメータの追加によってネットワークの性能が飛躍的に向上することを示しました。量子機械学習は、量子力学の特性を活用して高速かつ効果的な処理を可能にします。この研究は、量子機械学習のトレーニングプロセスの最適化と実用化に向けた重要な進展です。
<関連情報>
量子ニューラルネットワークにおけるオーバーパラメトリゼーションの理論 Theory of overparametrization in quantum neural networks
Martín Larocca,Nathan Ju,Diego García-Martín,Patrick J. Coles & Marco Cerezo
Nature Computational Science Published:26 June 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43588-023-00467-6
Abstract
The prospect of achieving quantum advantage with quantum neural networks (QNNs) is exciting. Understanding how QNN properties (for example, the number of parameters M) affect the loss landscape is crucial to designing scalable QNN architectures. Here we rigorously analyze the overparametrization phenomenon in QNNs, defining overparametrization as the regime where the QNN has more than a critical number of parameters Mc allowing it to explore all relevant directions in state space. Our main results show that the dimension of the Lie algebra obtained from the generators of the QNN is an upper bound for Mc, and for the maximal rank that the quantum Fisher information and Hessian matrices can reach. Underparametrized QNNs have spurious local minima in the loss landscape that start disappearing when M ≥ Mc. Thus, the overparametrization onset corresponds to a computational phase transition where the QNN trainability is greatly improved. We then connect the notion of overparametrization to the QNN capacity, so that when a QNN is overparametrized, its capacity achieves its maximum possible value.