2022-03-01 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL),パウル・シェラー研究所(PSI)
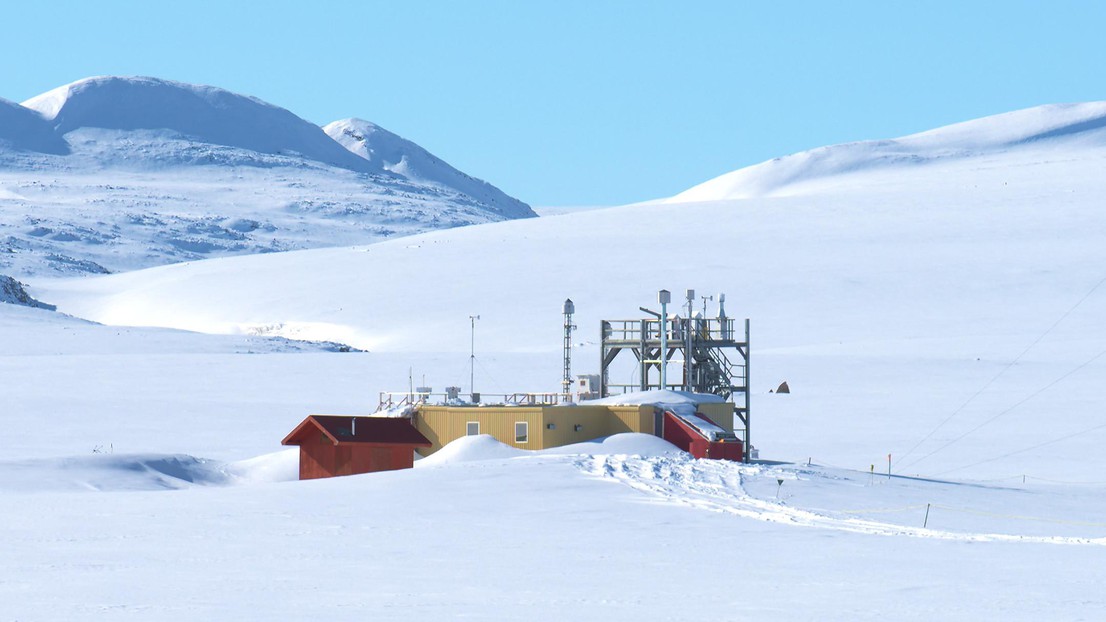

Alert Research Station, Canada ,1 June 2016. © Kevin Rawlings
Scientists at EPFL and the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have studied the chemical composition and origin – whether natural or anthropogenic – of aerosols in a region spanning from Russia to Canada. Their findings provide unique insights for helping researchers better understand climate change in the Arctic and design effective pollution-mitigation measures. The work was made possible thanks to the joint effort of scientists from three continents.
The tiny particles suspended in the air known as aerosols play an important role in heating and cooling our planet, but their effects still aren’t fully understood. The particles can occur naturally, such as from volcanoes, forests and oceans, or be produced by human activity, such as fossil-fuel combustion and industrial manufacturing. They interact with solar radiation, either reflecting it back out into space and lowering the Earth’s temperature, or absorbing it and raising the temperature. They are also essential for the formation of clouds, which similarly play a role in cooling off or warming up the planet by reflecting solar radiation out into space or re-emitting terrestrial radiation back down to the Earth. Cloud formation in the Arctic is particularly sensitive to aerosols.
To gain deeper insight into these mechanisms, scientists at ENAC’s Extreme Environments Research Laboratory, headed by tenure-track assistant professor Dr. Julia Schmale, and the PSI’s Laboratory of Atmospheric Chemistry, whose Research Laboratory Head is Dr. Imad El Haddad, analyzed samples taken from eight research stations across the Arctic over several years. The Arctic is a crucial region for understanding climate change because the temperature there is rising two to three times faster than the rest of the planet. “If we know what kind of aerosols exist in different areas and at different times of year, and what the origin and composition of those aerosols are, we will have a better grasp of how they contribute to climate change,” says Schmale. “That will also help us design more targeted measures to reduce pollution.” The study was led by Vaios Moschos as part of his PhD thesis, supervised jointly by Schmale and El Haddad.
Anthropogenic in the winter and natural in the summer
In a first study, Moschos et al. looked specifically at organic aerosols. Scientists still have little data on these aerosols even though they make up nearly 50% of total particulate matter. The researchers in this study analyzed the chemical composition of samples taken in the Arctic and found that, in the winter, most of those aerosols come from human activity. They attribute this to the Arctic haze that occurs each year when emissions from oil extraction and mining operations in North America, Eastern Europe and Russia are carried to the Arctic and trapped there during the winter.
On the other hand, the study found that most organic aerosols in the summer come from natural sources. That’s because the transport of anthropogenic aerosols from mid-latitudes to the Arctic is diminished during the warmer months, and the high latitude emission rate of biogenic aerosols or their precursors rises. “We didn’t expect to see so much naturally occurring organic aerosols,” says Schmale. “These particles come from boreal forests as well as phytoplankton, a micro-organism that lives in oceans. Here we might see a consequence of global warming in the future – as forests expand northwards and the permafrost thaws more organic molecules can be released from land, and as sea ice retreats, more open ocean leaves space for microbial emissions.”
Mitigation is now possible
In another study, the EPFL and PSI scientists used the same samples but analyzed the composition and origin of all the aerosols, both organic and inorganic. They found that the inorganic aerosols included black carbon, sulfate and sea salt; black carbon is of particular concern to the scientific community because it absorbs solar radiation and contributes to global warming. “We knew that black carbon emissions were high in regions with oil and gas extraction facilities, but we didn’t have collocated pan-Arctic measurements to understand how large their circle of influence is,” says Schmale. “Thanks to the data collected in this study, we were able to map black carbon concentrations and origins in each Arctic region throughout the year and recommend the most appropriate measures to take.”
The scientists were able to perform the studies thanks to a unique joint effort bringing together scientists from Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, India, Italy, Norway, Russia, Slovenia and the US. The eight research stations at which samples were collected (see list below) are run by research groups from various countries. The samples were analyzed at the two labs in Switzerland. El Haddad explains: “Analyzing organic aerosols requires mass spectrometers, which are expensive, sophisticated instruments, along with trained experts. That’s one reason why we still have little data from the Arctic on this subject. Our lab is at the forefront of research on organic aerosols and their origin.”
Samples were collected at the following research stations:
- Alert, Canada
- Baranova, Russia
- Gruvebadet, Norway
- Pallas, Finland
- Tiksi, Russia
- Utqiagvik, USA
- Villum, Greenland
- Zeppelin, Norway
Funding
This research has received funding from:
– The European Union’s Horizon 2020 Framework Programme 231 via the ERA-PLANET (The European Network for observing our changing Planet) project iCUPE 232 (Integrative and Comprehensive Understanding on Polar Environments) under grant agreement No. 233 689443
– The Swiss State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI; contract No. 234 15.0159-1)
– The SNSF Scientific Exchanges grant “Source apportionment of Russian Arctic aerosols,” 237 (SARAA; No. 187566)
References
Moschos, V., Schmale, J. K., Aas, W., Becagli, S., Calzolai, G., Eleftheriadis, K., Moffett, C. E., Schnelle-Kreis, J., Severi, M., Sharma, S., Skov, H., Vestenius, M., Zhang, W., Hakola, H., Hellen, H., Huang, L., Jaffrezo, J. L., Massling, A., Nojgaard, J., Petaja, T., Popovicheva, O., Sheesley, R. J., Traversi, R., Yttri, K. E., Prevot, A. S. H., Baltensperger, U., and El Haddad, I.: “Elucidating the present-day chemical composition, seasonality and source regions of climate-relevant aerosols across the Arctic land surface”, Environmental Research Letters, 2022, 10.1088/1748-9326/ac444b
Moschos, V., Dzepina, K., Bhattu, D., Lamkaddam, H., Casotto, R., Daellenbach, K. R., Canonaco, F., Aas, W., Becagli, S., Calzolai, G., Eleftheriadis, K., Moffett, C. E., Schnelle-Kreis, J., Severi, M., Sharma, S., Skov, H., Vestenius, M., Zhang, W., Hakola, H., Hellen, H., Huang, L., Jaffrezo, J. L., Massling, A., Nojgaard, J., Petaja, T., Popovicheva, O., Sheesley, R. J., Traversi, R., Yttri, K. E., Schmale, J., Prevot, A. S. H., Baltensperger, U., and El Haddad, I.: “Equal abundance of summertime natural and wintertime anthropogenic Arctic organic aerosols”, Nature Geoscience, 2022, 10.1038/s41561-021-00891-1
Abstract
Aerosols play an important yet uncertain role in modulating the radiation balance of the sensitive Arctic atmosphere. Organic aerosol is one of the most abundant, yet least understood, fractions of the Arctic aerosol mass. Here we use data from eight observatories that represent the entire Arctic to reveal the annual cycles in anthropogenic and biogenic sources of organic aerosol. We show that during winter, the organic aerosol in the Arctic is dominated by anthropogenic emissions, mainly from Eurasia, which consist of both direct combustion emissions and long-range transported, aged pollution. In summer, the decreasing anthropogenic pollution is replaced by natural emissions. These include marine secondary, biogenic secondary and primary biological emissions, which have the potential to be important to Arctic climate by modifying the cloud condensation nuclei properties and acting as ice-nucleating particles. Their source strength or atmospheric processing is sensitive to nutrient availability, solar radiation, temperature and snow cover. Our results provide a comprehensive understanding of the current pan-Arctic organic aerosol, which can be used to support modelling efforts that aim to quantify the climate impacts of emissions in this sensitive region.