2026-02-12 東京農工大学
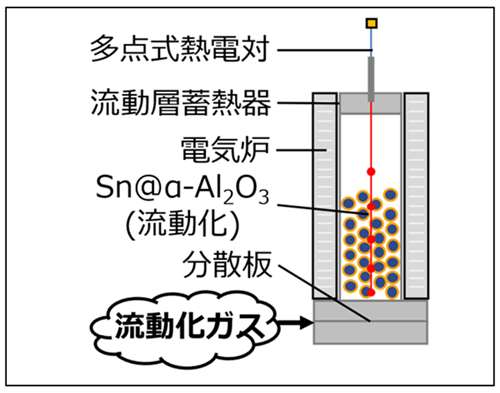
図1:流動層実験装置図
<関連情報>
- https://www.tuat.ac.jp/outline/disclosure/pressrelease/2025/20260212_02.html
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5c03913
流動床におけるSn@α-Al 2O3マイクロカプセル化相変化材料(MEPCM)の熱的および物理的特性 Thermal and Physical Properties of Sn@α-Al2O3 Microencapsulated Phase Change Material (MEPCM) in a Fluidized Bed
Masahiro I. Aoki,Takuto Aoki,Naoya Shirota,Tomokazu Nakamura,Melbert Jeem,Takahiro Nomura,and Chihiro Fushimi
Energy & Fuels Published: December 4, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5c03913
Abstract
This study investigates the heat storage and release, and durability characteristics of microencapsulated phase change material (MEPCM) particles (average size: 31 μm) comprising an Sn core and α-Al2O3 shell (Sn@α-Al2O3) in a fluidized bed (i.d.: 29.8 mm, bed height: 90 mm). The MEPCM is designed to store latent heat at approximately 239 °C, targeting medium-to-high temperature waste heat recovery. Heat charge and discharge experiments were conducted by fluidizing the particle bed by varying the gas velocity to two times higher than the minimum fluidization velocity (umf) and measuring the axial temperature profile. The results showed rapid and uniform heat transfer during both the charging and discharging processes without observable temperature stratification in the bed when the gas velocity was 1.5 times or higher than umf. Particle durability was evaluated under high-temperature fluidization above 300 °C for 40 h. Elemental mapping indicated partial shell degradation and Sn oxidation after prolonged operation. However, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) analysis confirmed that the latent heat capacity was retained even after 30 h of fluidization. These findings suggest that Sn@α-Al2O3 MEPCM particles can be applied to medium-temperature thermal energy storage (approximately 100–300 °C) in fluidized beds, offering both rapid thermal response and acceptable durability for waste heat recovery applications.