2026-02-05 中国科学院(CAS)
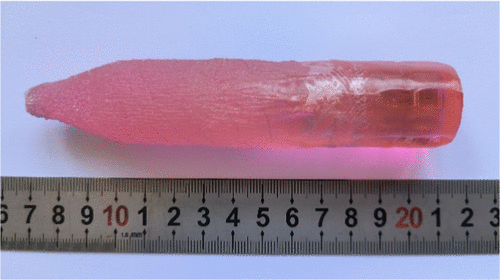
Photograph of the as-grown Er:GdLuYSGG crystal (Image by ZHANG Huili)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research-news/202602/t20260210_1150429.shtml
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.cgd.5c01447
高エントロピーEr:GdLuYSGG結晶の構造、分光法および2.8μmレーザー性能の向上 Structure, Spectroscopy and Enhanced 2.8 μm Laser Performance of a High-Entropy Er:GdLuYSGG Crystal
Huili Zhang,Dunlu Sun,Cong Quan,Maojie Cheng,Kunpeng Dong,Zhentao Wang,Hongyuan Li,and Xinjie Li,Shiji Dou
Crystal Growth & Design Published: December 26, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.5c01447
Abstract
A novel high-entropy laser crystal of 30 at. % Er:GdLuYSGG was grown by the Cz method. The crystal exhibits high crystalline quality, evidenced by an X-ray rocking curve FWHM of 0.007°. The thermal expansion coefficient and thermal conductivity are determined to be 1.52 × 10–5 K–1 and 4.10 W m–1 K–1, respectively. A broadened fluorescence band around 2760–2840 nm is observed and attributed to the lattice distortion effect of the high-entropy crystal, indicating the Er:GdLuYSGG crystal is beneficial for realizing tunable or ultrafast lasers. By a 973 nm LD end-pumping, a continuous-wave 2.8 μm laser is achieved with a maximum output power of 1062 mW, corresponding to a slope efficiency of 17.99%. The Mx2/My2 factors are 1.35 and 1.37, suggesting a high laser beam quality. The results imply that the high-entropy Er:GdLuYSGG crystal is a promising broadband gain medium for high-performance 2.8 μm mid-infrared laser, which might be particularly suited for applications in space radiation environments.