2026-01-21 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
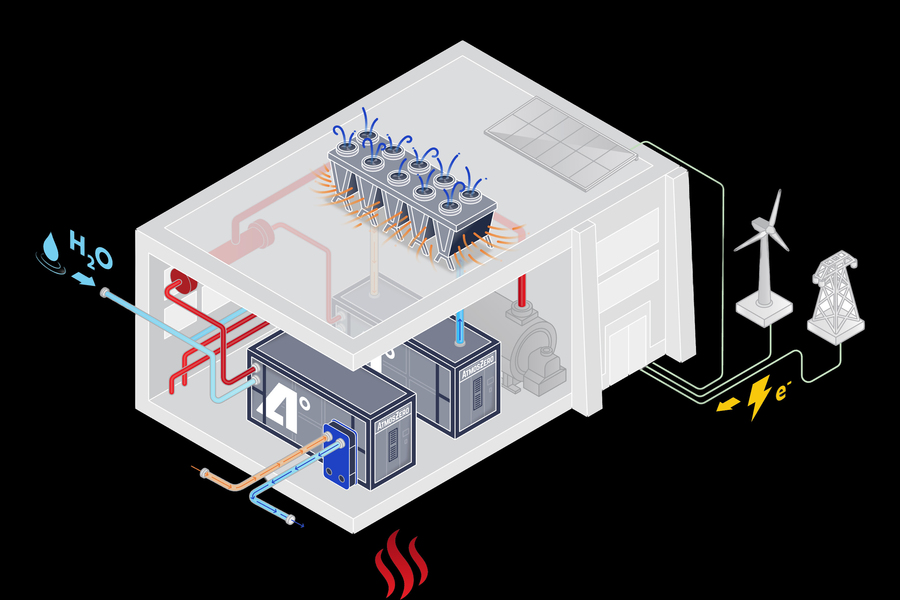 “Steam is the most important working fluid ever,” says AtmosZero co-founder Addison Stark.Credit: Courtesy of AtmosZero
“Steam is the most important working fluid ever,” says AtmosZero co-founder Addison Stark.Credit: Courtesy of AtmosZero
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2026/atmoszero-electrifies-boilers-to-decarbonize-industry-0121
- https://www.cell.com/joule/fulltext/S2542-4351(20)30575-4
産業の脱炭素化には熱の脱炭素化が必要だ To decarbonize industry, we must decarbonize heat
Gregory P. Thiel ∙ Addison K. Stark
Joule Published:January 6, 2021
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2020.12.007
Context & scale
Industry is often termed “hard to decarbonize” because a vast, inhomogeneous array of processes comprise the sector. Nevertheless, decarbonization of the industrial sector is crucial to addressing economy-wide emissions. In 2010, a full 13.1 gigatons (Gt) of carbon dioxide (CO2) and 176 exajoules (EJ) of primary energy demand were attributed to the sector globally. Developing new, decarbonized process heating technologies represents a single, broadly applicable pathway to eliminating a large portion of sectoral emissions, and approximately one-fifth of global CO2 emissions, overall.
In this perspective, we propose a cross-cutting research effort in (1) zero-carbon heat, (2) electrification of heat, (3) zero-carbon fuels, and (4) better heat management. If pursued, these distinct and cross-cutting areas for R&D will help drive technical advances that can help further reduce industrial heat emissions, such that neither economic nor climate progress are sacrificed.
Highlights
- Decarbonizing the industrial sector is a key part of economy-wide decarbonization
- Decarbonizing process heat alone can mitigate about a fifth of global CO2 emissions
- Cross-cutting R&D that can decarbonize industrial process heat is identified
Summary
Industry is often termed “hard to decarbonize” because a vast, inhomogeneous array of processes comprise the sector. But developing new, decarbonized process heating technologies represents a single, broadly applicable pathway to eliminating a large portion of sectoral emissions—and approximately one-fifth of global CO2 emissions, overall. We begin this perspective with a brief review of the demand for and cost of industrial heat. Then, we highlight key challenges and R&D needs in developing zero-carbon industrial heating technologies. Technologies in four pathways are discussed: (1) zero-carbon fuels, (2) zero-carbon heat sources, (3) electrification of heat, and (4) better heat management. Finally, we identify cross-cutting challenges to the development and adoption of zero-carbon industrial heat technologies, the solution to any of which would constitute a significant breakthrough on the path to industrial decarbonization.



