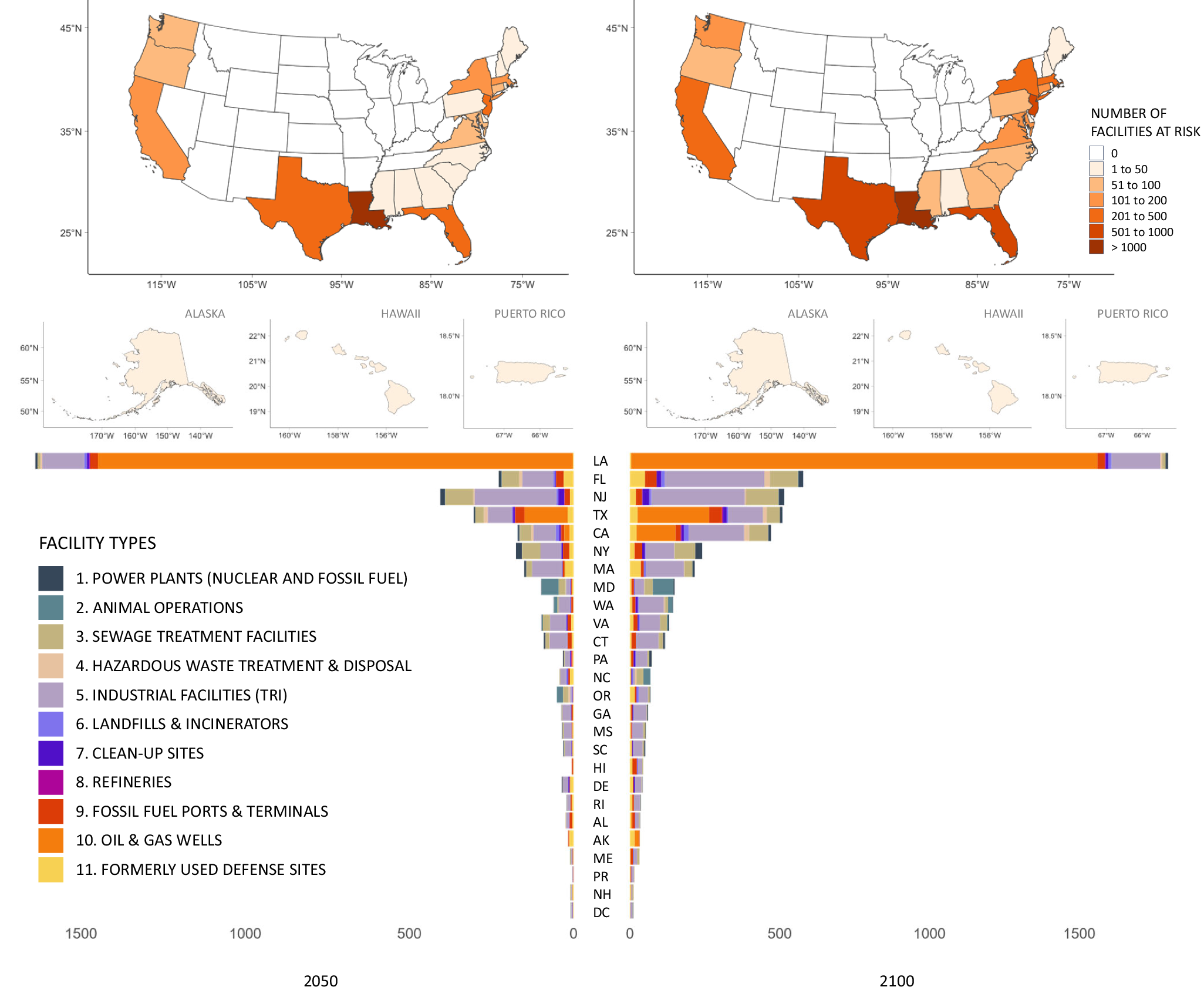
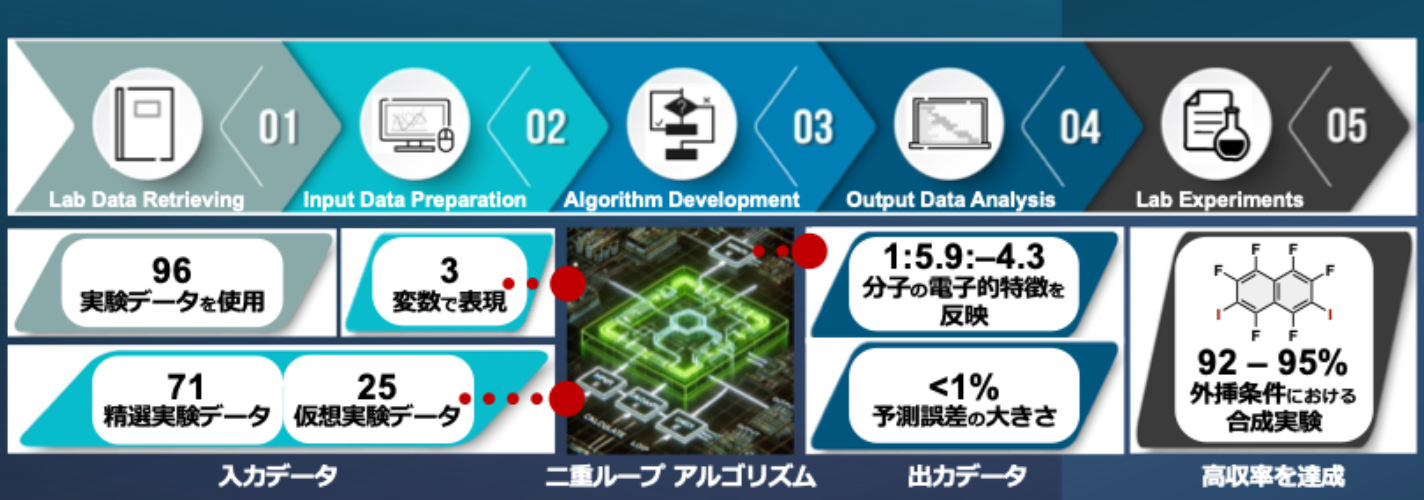
2025-11-20 大阪大学

<関連情報>
- https://www.sci.osaka-u.ac.jp/ja/topics/16051/
- https://www.sci.osaka-u.ac.jp/ja/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/pr_takada.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-64876-z
電子チャネル遮断によるプラズモン波束の固有状態制御 Eigenstate control of plasmon wavepackets with electron-channel blockade
Shintaro Takada,Giorgos Georgiou,Junliang Wang,Yuma Okazaki,Shuji Nakamura,David Pomaranski,Arne Ludwig,Andreas D. Wieck,Michihisa Yamamoto,Christopher Bäuerle & Nobu-Hisa Kaneko
Nature communications Published:12 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-64876-z
Abstract
Coherent manipulation of plasmon wavepackets in solid-state systems is crucial for advancing nanoscale electronic devices, offering a unique platform for quantum information processing based on propagating quantum bits. Controlling the eigenstate of plasmon wavepackets is essential, as it determines their propagation speed and hence the number of quantum operations that can be performed during their flight time through a quantum system. When plasmon wavepackets are generated by short voltage pulses and transmitted through nanoscale devices, they distribute among multiple electron conduction channels via Coulomb interactions, a phenomenon known as charge fractionalisation. This spreading complicates plasmon manipulation in quantum circuits and makes precise control of the eigenstates of plasmon wavepackets challenging. Using a cavity, we demonstrate the ability to isolate and select electron conduction channels contributing to plasmon excitation, thus enabling precise control of plasmon eigenstates. Specifically, we observe an electron-channel blockade effect, where charge fractionalisation into cavity-confined channels is suppressed due to the plasmon’s narrow energy distribution, enabling more stable and predictable plasmonic circuits. This technique provides a versatile tool for designing plasmonic circuits, offering the ability to tailor plasmon speed through local parameters, minimise unwanted plasmon excitation in adjacent circuits, and enable the precise selection of electron-channel plasmon eigenstates in quantum interferometers.