2025-11-05 千葉工業大学
Web要約 の発言:
<関連情報>
- https://chibatech.jp/news/imolkd0000004c3f-att/pressanalog.pdf
- https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/aisy.202500351
アナログインメモリコンピューティング回路における非理想性の活用:ニューロモルフィックシステムのための物理モデリングアプローチ Harnessing Nonidealities in Analog In-Memory Computing Circuits: A Physical Modeling Approach for Neuromorphic Systems
Yusuke Sakemi, Yuji Okamoto, Takashi Morie, Sou Nobukawa, Takeo Hosomi, Kazuyuki Aihara
Advanced Intelligent Systems Published: 18 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202500351
Abstract
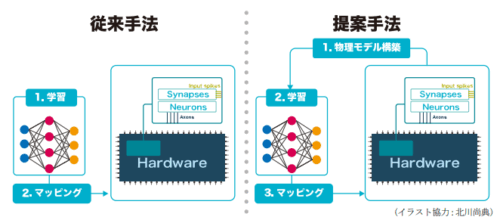
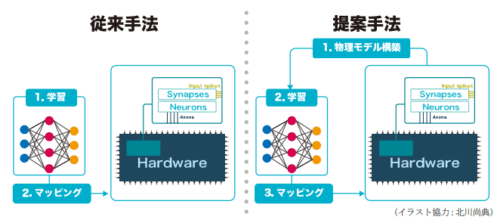
Large-scale deep learning models are increasingly constrained by their immense energy consumption, which limits their scalability and applicability for edge intelligence. In-memory computing (IMC) offers a promising solution by addressing the von Neumann bottleneck inherent in traditional deep learning accelerators, significantly reducing energy consumption. However, the analog nature of IMC introduces hardware nonidealities that degrade model performance and reliability. This article presents a novel approach to directly train physical models of IMC, formulated as ordinary differential equation (ODE)-based physical neural networks (PNNs). To enable the training of large-scale networks, a technique called differentiable spike-time discretization is proposed, which reduces the computational cost of ODE-based PNNs by up to 20 times in speed and 100 times in memory. Such large-scale networks enhance learning performance by exploiting hardware nonidealities on the CIFAR-10 dataset. The proposed bottom-up methodology is validated through post-layout SPICE simulations on the IMC circuit with nonideal characteristics using the sky130 process. The proposed PNN approach reduces the discrepancy between model behavior and circuit dynamics by at least an order of magnitude. This work paves the way for leveraging nonideal physical devices, such as nonvolatile resistive memories, for energy-efficient deep learning applications.