2025-10-31 北海道大学
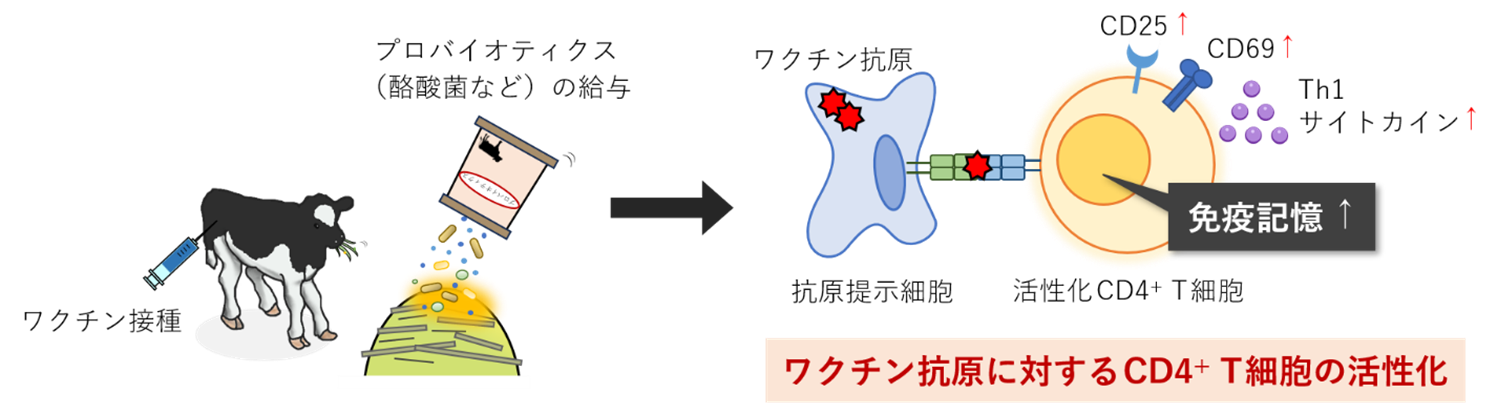
プロバイオティクスのワクチン応答増強効果
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/2025/10/post-2115.html
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/251031_pr3.pdf
- https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/13/11/1120
プロバイオティクス給与による子牛のワクチンに対するT細胞応答の増強 Enhancement of Vaccine-Induced T-Cell Responses by Probiotics in Calves
Mari Ikehata,Tomohiro Okagawa,Hayato Nakamura,Naoya Maekawa,Yasuhiko Suzuki,Shiro Murata,Kazuhiko Ohashi and Satoru Konnai
Vaccines Published: 31 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111120
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Calves have immature immune systems, hence immunization with vaccines is essential to protect them from infectious diseases. However, immune responses to vaccines vary widely among individuals. Therefore, strategies for enhancing vaccine efficacy are needed, particularly those targeting low responders to vaccines. Probiotics have attracted attention because of their beneficial immunomodulatory effects on the host. Although probiotics may improve calf immunity, their potential to enhance immune responses to vaccines in calves remains unclear. Thus, we investigated whether immune responses to vaccines, especially T-cell responses, are enhanced when calves receive a combination of probiotic supplementation and vaccination. Methods: Calves were divided into three feeding groups, as follows: negative control feed, live bacteria-mixed feed (Zeosapo KB), and Clostridium butyricum-only feed (CB). After weaning, all calves received two doses of a live attenuated hexavalent viral vaccine. T-cell responses to a vaccine antigen were evaluated by measuring the expression levels of lymphocyte activation markers CD25 and CD69, as well as Th1 cytokine production, in peripheral blood mononuclear cell culture assays. Results: CD25 expression significantly increased in CD4+ T cells four weeks after the booster vaccination in the Zeosapo KB- and CB-fed groups. In addition, the CD25+CD69+ cell ratio in CD4+ T cells was increased in these groups. The production of Th1 cytokines in the culture supernatant was also increased in the CB-fed group. Conclusions: This clinical study demonstrates that probiotics activate CD4+ T cells and enhance Th1 cytokine responses in vaccinated calves.