2025-07-24 東京科学大学
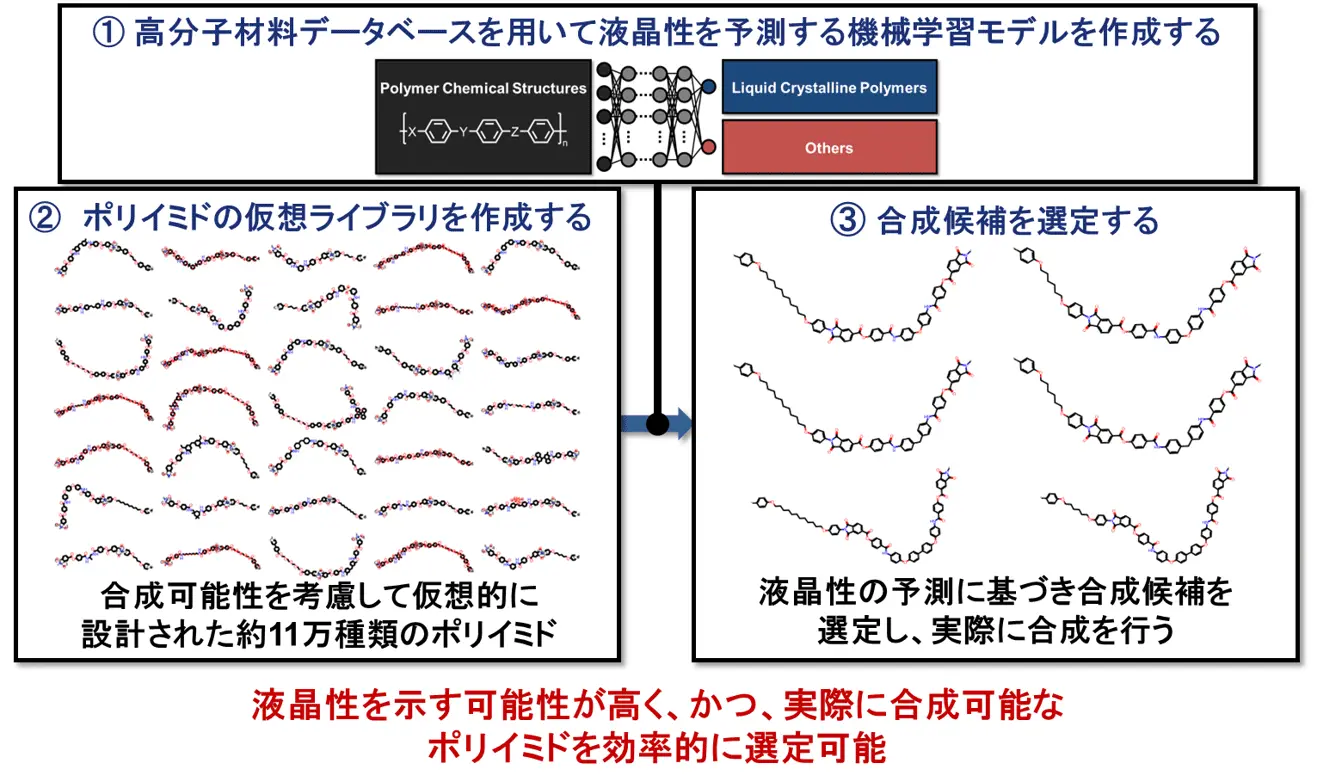 図1.機械学習を用いた液晶性ポリイミドの分子設計
図1.機械学習を用いた液晶性ポリイミドの分子設計
<関連情報>
機械学習を用いた高熱伝導率を有する液晶ポリマーの発見 Discovery of liquid crystalline polymers with high thermal conductivity using machine learning
Hayato Maeda,Stephen Wu,Rika Marui,Erina Yoshida,Kan Hatakeyama-Sato,Yuta Nabae,Shiori Nakagawa,Meguya Ryu,Ryohei Ishige,Yoh Noguchi,Yoshihiro Hayashi,Masashi Ishii,Isao Kuwajima,Felix Jiang,Xuan Thang Vu,Sven Ingebrandt,Masatoshi Tokita,Junko Morikawa,Ryo Yoshida & Teruaki Hayakawa
npj Computational Materials Published:02 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-025-01671-w
Abstract
Next-generation power electronics require efficient heat dissipation management, and molecular design guidelines are needed to develop polymers with high thermal conductivity. Polymer materials have considerably lower thermal conductivity than metals and ceramics due to phonon scattering in the amorphous region. The spontaneous orientation of the molecular chains of liquid crystalline polymers could potentially give rise to high thermal conductivity, but the molecular design of such polymers remains largely empirical. In this study, we developed a machine learning model that predicts with more than 96% accuracy whether liquid crystalline states will form based on the chemical structure of the polymer. By exploring the inverse mapping of this model, we identified a comprehensive set of chemical structures for liquid crystalline polyimides. The polymers were then experimentally synthesized, and the results confirmed that they form liquid crystalline phases, with all polymers exhibiting calculated thermal conductivities within the range of 0.722–1.26 W m−1 K−1.