2025-07-17 分子科学研究所
<関連情報>
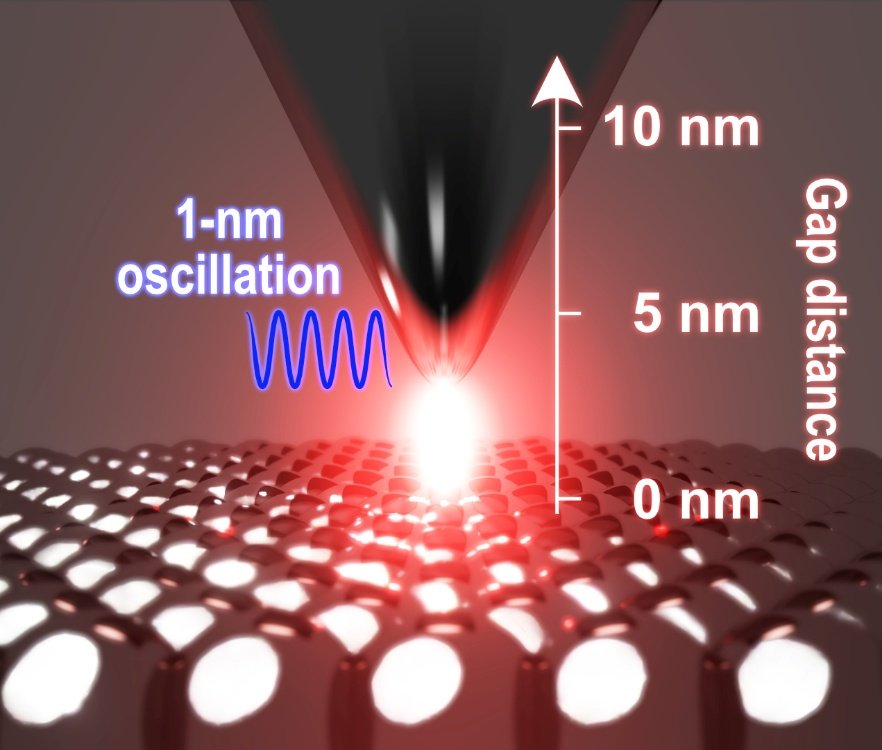
極小の探針振動振幅を用いた1ナノメートル分解能の散乱型近接場光顕微鏡法 Scattering near-field optical microscopy at 1-nm resolution using ultralow tip oscillation amplitudes
Akitoshi Shiotari, Jun Nishida, Adnan Hammud, Fabian Schulz, […] , and Melanie Müller
Science Advances Published:11 Jun 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adu1415
Abstract
Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) allows for the observation of the optical response of material surfaces with a resolution far below the diffraction limit. Based on amplitude-modulation atomic force microscopy (AFM) with typical tapping amplitudes of tens of nanometers, a spatial resolution of 10 to 100 nm is routinely achieved in s-SNOM. However, optical imaging and spectroscopy of atomic-scale structures remain a substantial challenge. Here, we developed ultralow tip oscillation amplitude s-SNOM (ULA-SNOM), where the ultraconfined field localized at a 1-nm-scale gap between a plasmonic tip and sample is combined with frequency-modulation (noncontact) AFM in a stable cryogenic ultrahigh vacuum environment. Using a silver tip under visible laser illumination with a constant 1-nm amplitude oscillation, we obtain a material-contrast image of silicon islands on a silver surface with 1-nm lateral resolution, which surpasses the conventional limits of s-SNOM. ULA-SNOM paves the way for the acquisition of optical information from atomic-scale structures, such as single photo-active defects and molecules.


