2025-06-30 名古屋大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.nagoya-u.ac.jp/researchinfo/result/2025/06/-x3400.html
- https://www.nagoya-u.ac.jp/researchinfo/result/upload_images/20250630_engg.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-05019-8
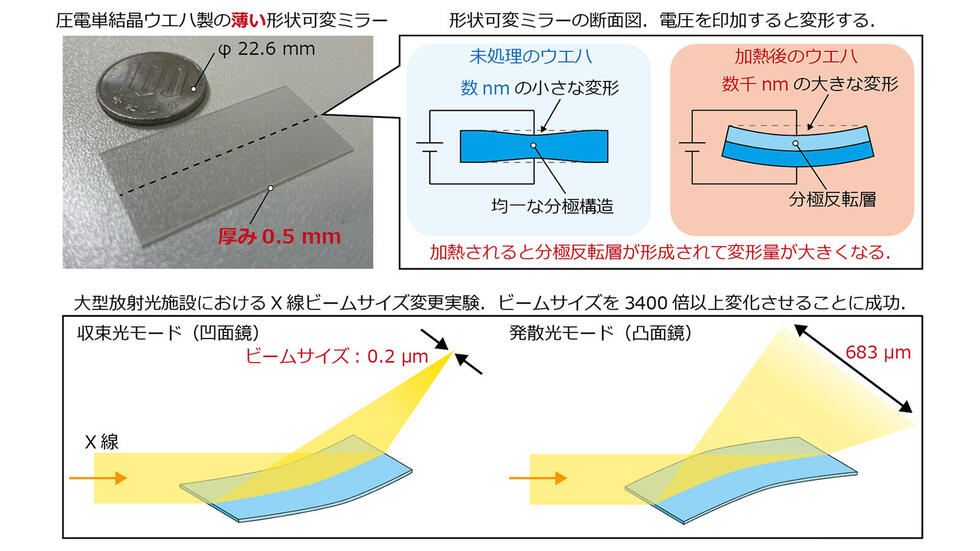
偏光反転ニオブ酸リチウムウエハーを用いた超薄型モノリシックバイモルフミラー Ultrathin monolithic bimorph mirror using polarization-inverted lithium niobate wafer
Takato Inoue,Junya Yoshimizu,Toma Ueyama,Maaya Kano,Yoshiki Kohmura,Makina Yabashi & Satoshi Matsuyama
Scientific Reports Published:27 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-05019-8
Abstract
Deformable mirrors (DMs) serve diverse applications and have been adopted in X-ray optics recently. DMs are being used in various X-ray optical systems with variable parameters, with piezoelectric bimorph mirrors favored the most. However, conventional bimorph mirrors have limited deformation capabilities. In this study, we propose a novel monolithic bimorph mirror that utilizes the polarization inversion properties of lithium niobate. Unlike traditional bimorph mirror designs that require bonding multiple materials, this approach allows for an extremely thin mirror that significantly enhances its deformation capabilities. Experimental fabrication of the mirror demonstrated a substantial curvature change of 0.1 m− 1. Furthermore, upon introduction of this novel mirror into SPring-8 as X-ray focusing optics, it achieved deformation to a target elliptical shape with a 1 μm peak-to-valley height and 3 nm precision. This accuracy and large deformation amount allowed for huge variation in the X-ray beam size from 200 nm to 683 μm. Such extensive beam size variability is offering significant potential for advancing X-ray analytical and imaging applications.