2025-05-21 大阪大学,神戸大学科学技術振興機構
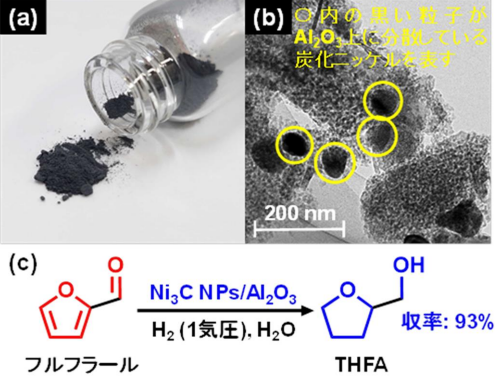
図 1. (a)開発した酸化アルミニウム担持炭化ニッケルナノ粒子触媒(Ni3C NPs/Al2O3)の写真, (b)電子顕微鏡像(黒い粒子が炭化ニッケルナノ粒子), (c)Ni3C NPs/Al2O3を用いた常圧水素下におけるフルフラール液相水素化反応.
<関連情報>
- https://www.jst.go.jp/pr/announce/20250521/index.html
- https://www.jst.go.jp/pr/announce/20250521/pdf/20250521.pdf
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5c01806
酸化アルミニウム担持炭化ニッケルナノ粒子触媒を用いたフルフラールおよびその誘導体のテトラヒドロフルフリル化合物への穏和かつ選択的水素化反応 Mild and Selective Hydrogenation of Furfural and Its Derivatives to Tetrahydrofurfuryl Compounds Catalyzed by Aluminum Oxide-supported Nickel Carbide Nanoparticles
Taiki Kawakami,Sho Yamaguchi,Satoshi Suganuma,Kiyotaka Nakajima,Takato Mitsudome,and Tomoo Mizugaki
ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering Published: May 20, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5c01806
Abstract
The hydrogenation of furfural (FUR), a representative lignocellulosic biomass-derived furanic compound, is a promising method for synthesizing tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol (THFA), which is used as a solvent and pharmaceutical intermediate. Significant efforts have been made to develop non-precious metal catalysts for the hydrogenation of FUR to THFA; however, these systems typically require harsh reaction conditions, such as high hydrogen pressure. In this study, we found that aluminum oxide-supported nickel carbide nanoparticles (Ni3C NPs/Al2O3) function as a highly active non-precious metal catalyst for the selective hydrogenation of FUR and its derivatives into the corresponding tetrahydrofuran derivatives with high yields. Notably, Ni3C NPs/Al2O3 enables the hydrogenation of FUR to THFA with over 90% yield even at 0.1 MPa of H2. The Ni3C NPs/Al2O3 catalyst also demonstrated effectiveness in gram–scale reactions. Control experiments and structural characterizations revealed its unique catalytic properties: polar hydrogen species formed on the Ni3C NPs surface efficiently reduce the aldehyde moiety of FUR, while cooperative effect at the Ni3C NPs–Al2O3 interface is essential to promoting the hydrogenation of a furan ring. These properties significantly enhance the catalytic performance of Ni3C NPs/Al2O3.