2025-05-12 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/a-step-towards-understanding-machine-intelligence-/
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.02280
LLM言語ネットワーク 神経科学的アプローチによるタスク関連ユニットの同定 The LLM Language Network: A Neuroscientific Approach for Identifying Causally Task-Relevant Units
Badr AlKhamissi, Greta Tuckute, Antoine Bosselut, Martin Schrimpf
arXive last revised 13 Feb 2025 (this version, v2)
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2411.02280
Abstract
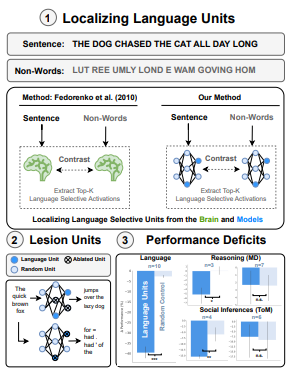
Large language models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities on not just language tasks, but also various tasks that are not linguistic in nature, such as logical reasoning and social inference. In the human brain, neuroscience has identified a core language system that selectively and causally supports language processing. We here ask whether similar specialization for language emerges in LLMs. We identify language-selective units within 18 popular LLMs, using the same localization approach that is used in neuroscience. We then establish the causal role of these units by demonstrating that ablating LLM language-selective units — but not random units — leads to drastic deficits in language tasks. Correspondingly, language-selective LLM units are more aligned to brain recordings from the human language system than random units. Finally, we investigate whether our localization method extends to other cognitive domains: while we find specialized networks in some LLMs for reasoning and social capabilities, there are substantial differences among models. These findings provide functional and causal evidence for specialization in large language models, and highlight parallels with the functional organization in the brain.