2025-04-24 パシフィック・ノースウェスト国立研究所(PNNL)
<関連情報>
- https://www.pnnl.gov/news-media/its-time-get-comfortable-uncertainty-ai-model-training
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41524-025-01572-y
ニューラルネットワーク潜在基礎モデルの不確実性定量化 Uncertainty quantification for neural network potential foundation models
Jenna A. Bilbrey,Jesun S. Firoz,Mal-Soon Lee & Sutanay Choudhury
npj Computational Materials Published:24 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-025-01572-y
Abstract
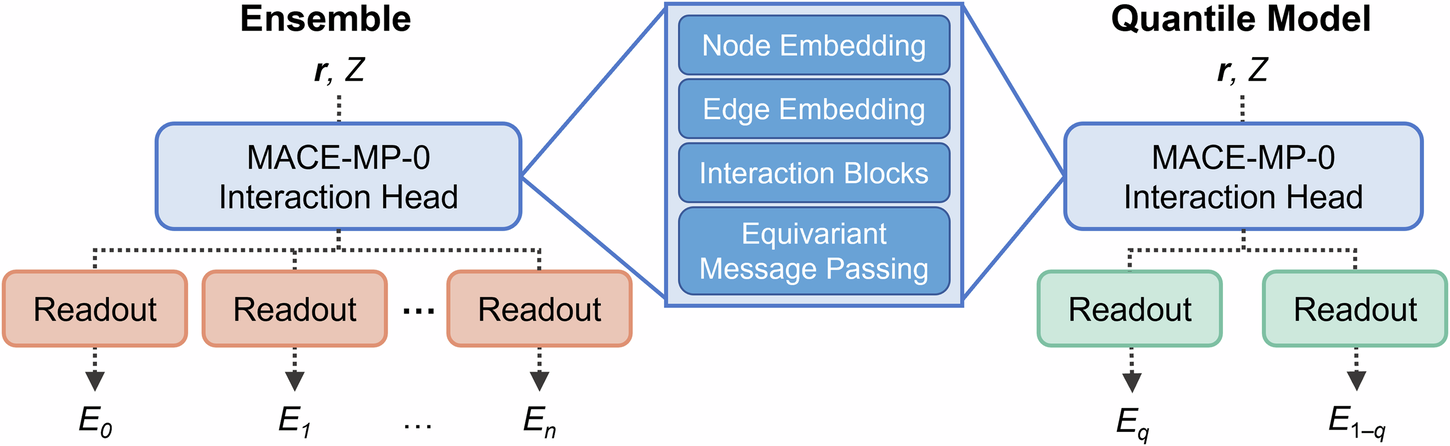
For neural network potentials (NNPs) to gain widespread use, researchers must be able to trust model outputs. However, the blackbox nature of neural networks and their inherent stochasticity are often deterrents, especially for foundation models trained over broad swaths of chemical space. Uncertainty information provided at the time of prediction can help reduce aversion to NNPs. In this work, we detail two uncertainty quantification (UQ) methods. Readout ensembling, by finetuning the readout layers of an ensemble of foundation models, provides information about model uncertainty, while quantile regression, by replacing point predictions with distributional predictions, provides information about uncertainty within the underlying training data. We demonstrate our approach with the MACE-MP-0 model, applying UQ to the foundation model and a series of finetuned models. The uncertainties produced by the readout ensemble and quantile methods are demonstrated to be distinct measures by which the quality of the NNP output can be judged.