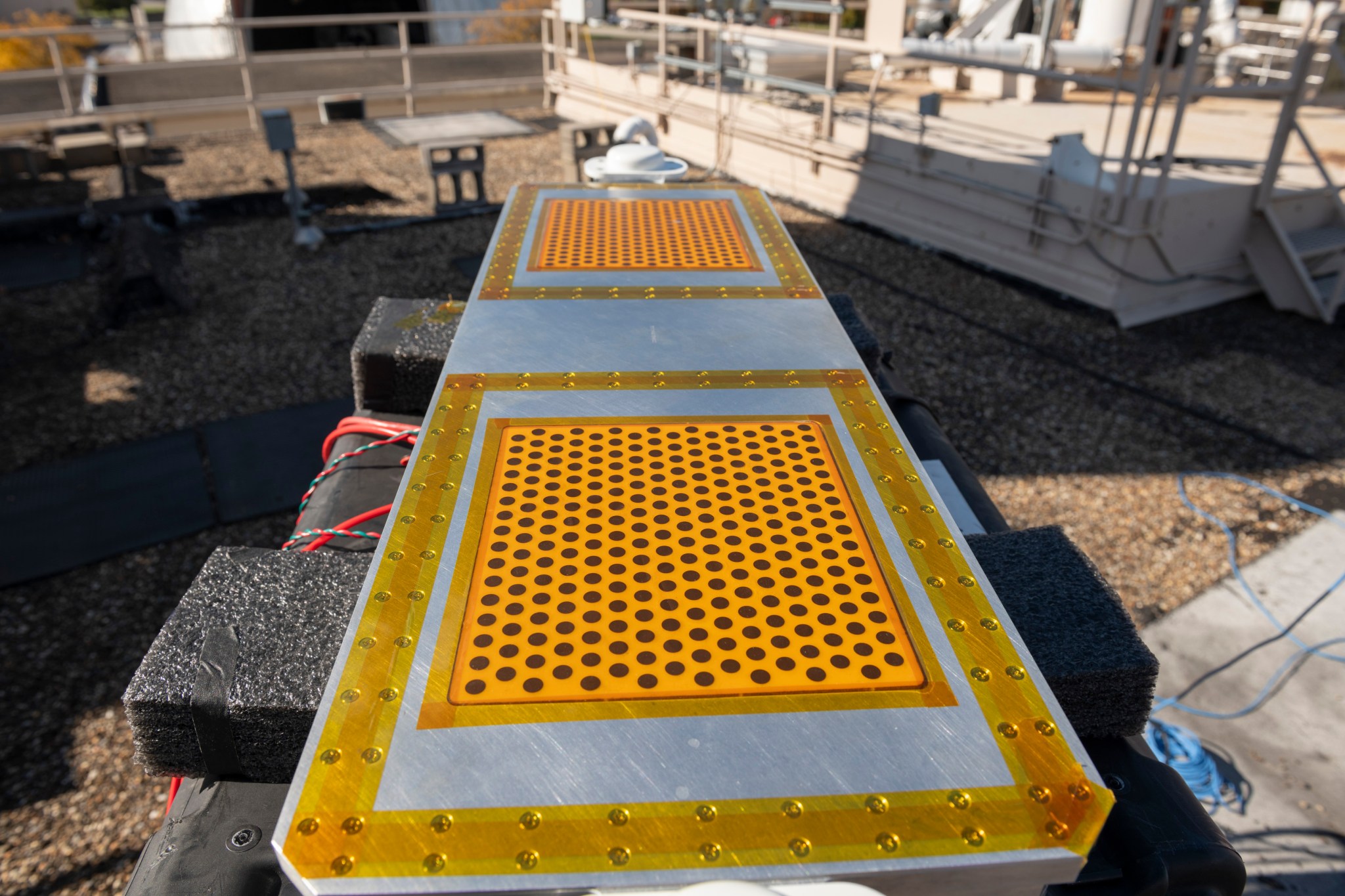
2025-04-22 ニューヨーク州立大学バッファロー校 (UB)
<関連情報>
- https://www.buffalo.edu/news/releases/2025/04/capturing-forever-chemicals-as-they-evaporate.html
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0003267025001400
固相マイクロ抽出法による気相および水相からの揮発性ペルフルオロアルキルおよびポリフルオロアルキル物質の効果的な前濃縮 Effective preconcentration of volatile per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances from gas and aqueous phase via solid phase microextraction
Héctor Martínez-Pérez-Cejuela, Madison L. Williams, Chloe McLeod, Emanuela Gionfriddo
Analytica Chimica Acta Available online: 31 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2025.343746
Graphical abstract

Highlights
- SPME effectively preconcentrates FTOHs, FOSAs, and FOSE from aqueous samples.
- Solventless thermal desorption of PFAS enhanced method performance.
- HS- and DI-SPME methods were optimized and applied to simulated seawater.
- SPME-GC-MS quantified volatile PFAS at parts-per-trillion concentrations.
Abstract
Background
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are synthetic fluorinated chemicals of increasing global concern due to their persistence, toxicity, and widespread presence in the environment. Neutral and volatile PFAS, used in firefighting foams and non-stick coatings, are precursors of perfluorinated acids such as perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and necessitate effective preconcentration methods for isolation from aqueous and gaseous phases.
Results
In this work, a robust quantitative method was rigorously optimized and validated to achieve effective preconcentration and quantification of neutral volatile PFAS, including fluorotelomer alcohols (FTOHs), perfluorooctanesulfonamides (FOSAs), and a perfluorooctanesulfonamido-ethanol (FOSE). Leveraging the versatility of solid phase microextraction (SPME) for sampling in different extraction modes, volatile PFAS were pre-concentrated in gaseous (Headspace-SPME) and aqueous (Direct Immersion-SPME) phases. The impact of temperature, time, and aqueous media composition on extraction efficiency was assessed, with analysis performed using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. LOQs between 0.005 μg L−1 and 5 μg L−1 were achieved for direct immersion-SPME and 0.005 μg L−1 to 0.25 μg L−1 for headspace-SPME, also demonstrating excellent repeatability with relative standard deviations (RSD%) below 11 %.
Significance
This work highlights the need for efficient pre-chromatographic separation methods for extraction and preconcentration of volatile PFAS. The developed Headspace and Direct Immersion-SPME methods provide a practical, solvent-free, automated solution for extraction and preconcentration of volatile PFAS from aqueous and gaseous samples. These methods enrich the analytical toolbox for PFAS analysis and can be applied to understanding how PFAS enter the environment and partition in heterogeneous systems.