2025-03-25 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202503/t20250321_908534.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-57750-5
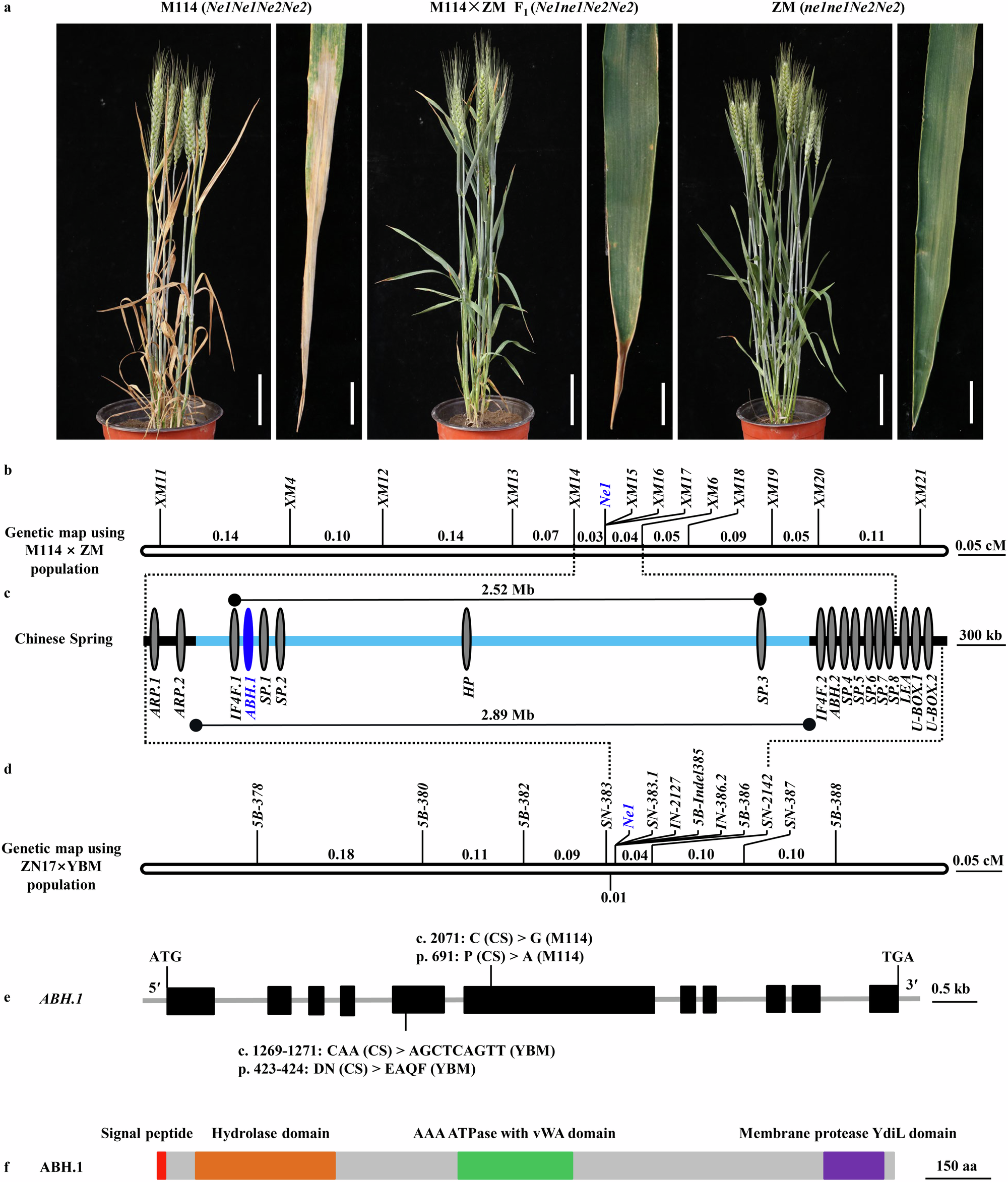
α/βヒドロラーゼのゲノム構造変異がコムギの雑種壊死を誘発する Genomic structural variation in an alpha/beta hydrolase triggers hybrid necrosis in wheat
Yaoqi Si,Huaizhi Zhang,Shengwei Ma,Shusong Zheng,Jianqing Niu,Shuiquan Tian,Xuejia Cui,Keyu Zhu,Xiaocui Yan,Qiao Lu,Zhimeng Zhang,Tingting Du,Ping Lu,Yongxing Chen,Qiuhong Wu,Jingzhong Xie,Guanghao Guo,Mengjun Gu,Huilan Wu,Yiwen Li,Chengguo Yuan,Zaifeng Li,Zhiyong Liu,Lingli Dong,… Miaomiao Li
Nature Communications Published:18 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-57750-5
Abstract
Hybrid necrosis, a century-old mystery in wheat, is caused by complementary genes Ne1 and Ne2. Ne2, encoding a nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat (NLR) immune receptor, has been cloned, yet Ne1 remains elusive. Here, we report that Ne1, which encodes an alpha/beta hydrolase (ABH) protein generated by structural variation, triggers hybrid necrosis with Ne2 by activating autoimmune responses. We further verify that not only allelic variation but also copy number variation (CNV) of Ne1 are pivotal for hybrid necrosis diversity in wheat. Ne1 likely originates from wild emmer wheat, potentially through duplication and ectopic recombination events. Unlike Ne2, which is frequently selected for rust resistance in wheat breeding, the lower prevalence of Ne1 in modern wheat cultivars is attributed to its association with hybrid necrosis. Altogether, these findings illuminate the co-evolution of the NLR/ABH gene pair in plant development and innate immunity, offering potential benefits for wheat breeding.



