2025-03-17 産業技術総合研究所
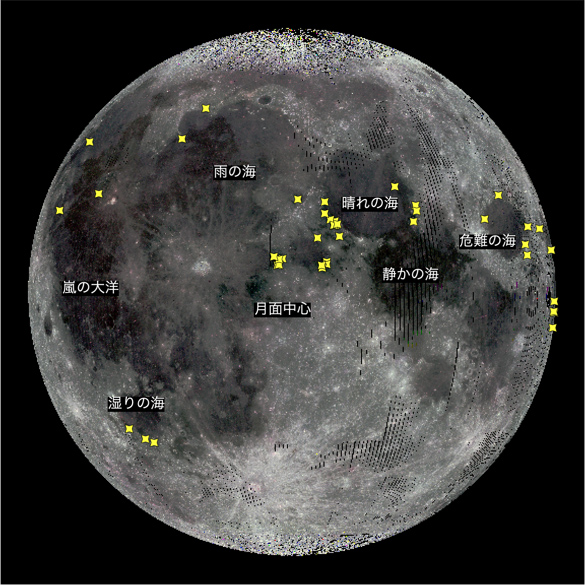

月面のチタン鉄鉱に富む地域(黄色印)の分布図
背景は月の明るさマップ(月探査衛星「かぐや」(SELENE)のマルチバンドデータを使用して作成)。図中の暗い領域は玄武岩に覆われた「海」と呼ばれる領域で、いわゆる「うさぎの模様」に相当する。
※「かぐや」(SELENE)データアーカイブ(https://darts.isas.jaxa.jp/app/pdap/selene/index.html.ja)(ISAS/JAXA)で公開されているデータを加工して使用しています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.aist.go.jp/aist_j/press_release/pr2025/pr20250317_2/pr20250317_2.html
- https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2024JE008663
月表面におけるイルメナイトリッチサイトの全球分布と地質学的特徴 Global Distribution and Geological Features of Ilmenite-Rich Sites on the Lunar Surface
Satoru Yamamoto, Moe Matsuoka, Hiroshi Nagaoka, Makiko Ohtake, Ayame Ikeda
Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets Published: 10 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JE008663
Abstract
We studied the global distribution and geological features of lunar surface sites whose spectra indicate an ilmenite-rich composition. Hyperspectral data obtained by the Kaguya Spectral Profiler were used for data mining to identify diagnostic features of a 1- and 2-μm spectral reflectance of ilmenite, revealing the global distribution of sites showing ilmenite-rich spectra. The results show that regions with ilmenite-rich spectra are concentrated at the margins of impact basins on the lunar nearside, whereas no such regions are identified in the Feldspathic Highland Terrain or the South Pole-Aitken basin. Using multiband images and a digital terrain model obtained by the Kaguya Multiband Imager and Terrain Camera, we examined the geological features of each site showing ilmenite-rich spectra and found that most of the sites are distributed on pyroclastic deposits overlying highland materials. Spectra interpreted as glass-rich material are prevalent in and around areas having ilmenite-rich spectra. However, sites showing ilmenite-rich spectra do not correspond to mare regions with TiO2-rich basalts. These results may indicate that the concentration of ilmenite in pyroclastic deposits is high enough to exhibit diagnostic features of 1- and 2-μμm spectral reflectance of ilmenite, whereas the concentration in mare regions with TiO2-rich basalt is not. Since pyroclastic deposits are expected to be extensive, deep unconsolidated deposits of relatively block-free debris, resulting in high processing efficiency in the hydrogen reduction processes, our data may be useful for developing an efficient exploration strategy for ilmenite as a lunar resource.
Key Points
- We examined lunar surface sites whose spectra show an ilmenite-rich composition
- Most of the ilmenite-rich spectra are found on pyroclastic deposits in the margins of the lunar mare regions
- Our results would be useful in developing an efficient strategy for the exploration of ilmenite as a lunar resource
Plain Language Summary
Ilmenite is a potential source of oxygen and a lunar resource mineral for the construction of future crewed lunar bases. Such applications require information on the global distribution and geological characteristics of ilmenite-rich sites on the lunar surface. In this study, hyperspectral data were used to identify diagnostic features of ilmenite and reveal the global distribution of ilmenite-rich locations on the Moon. The results show that sites with ilmenite-rich spectra are found in the marginal areas of the impact basins on the nearside of the Moon, whereas no ilmenite-rich spectra are identified in the Feldspathic Highland Terrain and the South Pole-Aitken basin. At each site, most regions with ilmenite-rich spectra are distributed on volcanic, pyroclastic deposits; however, these regions do not correspond to mare regions with TiO2-rich basalts. These results suggest that pyroclastic deposits are one of the lunar surface materials with the highest concentration of ilmenite. Since pyroclastic deposits are expected to be extensive and deep unconsolidated deposits of relatively block-free debris, resulting in high processing efficiency in the hydrogen reduction processes, our data may be useful for an efficient exploration strategy for ilmenite as a lunar resource.