2024-04-10 アルゴンヌ国立研究所(ANL)
<関連情報>
- https://www.anl.gov/article/scientists-pioneer-autonomous-robotic-method-for-studying-liquids-suspended-in-air
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-023-01233-z
ロボット・ペンダントドロップ:μs分解、AI実行可能なXPCSのための無容器液体 Robotic pendant drop: containerless liquid for μs-resolved, AI-executable XPCS
Doga Yamac Ozgulbas,Don Jensen Jr.,Rory Butler,Rafael Vescovi,Ian T. Foster,Michael Irvin,Yasukazu Nakaye,Miaoqi Chu,Eric M. Dufresne,Soenke Seifert,Gyorgy Babnigg,Arvind Ramanathan & Qingteng Zhang
Light: Science & Applications Published:18 August 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-023-01233-z
Abstract
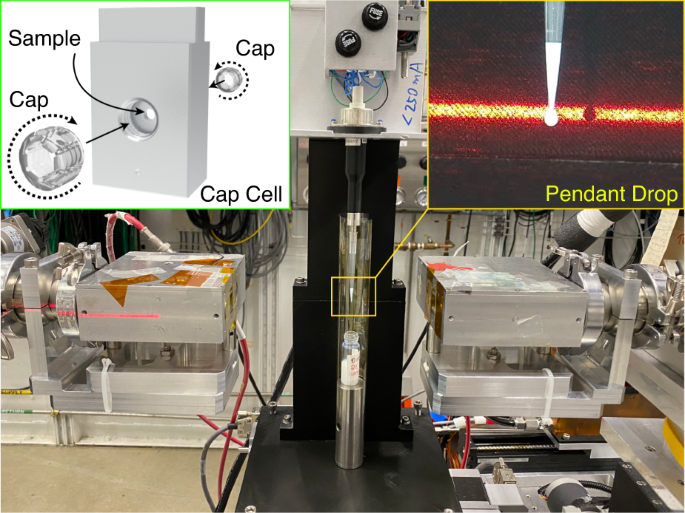
The dynamics and structure of mixed phases in a complex fluid can significantly impact its material properties, such as viscoelasticity. Small-angle X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (SA-XPCS) can probe the spontaneous spatial fluctuations of the mixed phases under various in situ environments over wide spatiotemporal ranges (10−6–103 s /10−10–10−6 m). Tailored material design, however, requires searching through a massive number of sample compositions and experimental parameters, which is beyond the bandwidth of the current coherent X-ray beamline. Using 3.7-μs-resolved XPCS synchronized with the clock frequency at the Advanced Photon Source, we demonstrated the consistency between the Brownian dynamics of ~100 nm diameter colloidal silica nanoparticles measured from an enclosed pendant drop and a sealed capillary. The electronic pipette can also be mounted on a robotic arm to access different stock solutions and create complex fluids with highly-repeatable and precisely controlled composition profiles. This closed-loop, AI-executable protocol is applicable to light scattering techniques regardless of the light wavelength and optical coherence, and is a first step towards high-throughput, autonomous material discovery.