2024-02-26 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
◆これにより、実世界のデータに適応し、偏りを持たずに予測を行うことが可能です。医療診断支援などのさまざまな実務タスクに適用され、特に資源の制約がある場合に有用です。
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/anything-in-anything-out-a-new-modular-ai-model/
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.14118
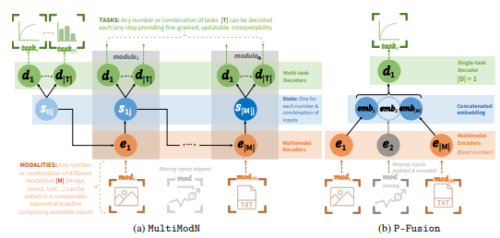
MultiModN- マルチモーダル、マルチタスク、解釈可能なモジュラーネットワーク MultiModN- Multimodal, Multi-Task, Interpretable Modular Networks
Vinitra Swamy, Malika Satayeva, Jibril Frej, Thierry Bossy, Thijs Vogels, Martin Jaggi, Tanja Käser, Mary-Anne Hartley
arXiv last revised:6 Nov 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2309.14118
Abstract
Predicting multiple real-world tasks in a single model often requires a particularly diverse feature space. Multimodal (MM) models aim to extract the synergistic predictive potential of multiple data types to create a shared feature space with aligned semantic meaning across inputs of drastically varying sizes (i.e. images, text, sound). Most current MM architectures fuse these representations in parallel, which not only limits their interpretability but also creates a dependency on modality availability. We present MultiModN, a multimodal, modular network that fuses latent representations in a sequence of any number, combination, or type of modality while providing granular real-time predictive feedback on any number or combination of predictive tasks. MultiModN’s composable pipeline is interpretable-by-design, as well as innately multi-task and robust to the fundamental issue of biased missingness. We perform four experiments on several benchmark MM datasets across 10 real-world tasks (predicting medical diagnoses, academic performance, and weather), and show that MultiModN’s sequential MM fusion does not compromise performance compared with a baseline of parallel fusion. By simulating the challenging bias of missing not-at-random (MNAR), this work shows that, contrary to MultiModN, parallel fusion baselines erroneously learn MNAR and suffer catastrophic failure when faced with different patterns of MNAR at inference. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first inherently MNAR-resistant approach to MM modeling. In conclusion, MultiModN provides granular insights, robustness, and flexibility without compromising performance.