2024-01-11 ロスアラモス国立研究所(LANL)
◆これにより、DALL-EやMidjourneyなどの既存モデルよりも少ない計算リソースで同等のサンプルが生成可能。離散空間で動作し、テキストや科学的アプリケーションに応用可能。科学的シミュレーションの時間を短縮し、超コンピュータ上での進歩を促進し、計算科学の炭素フットプリントを削減する可能性がある。
<関連情報>
ブラックアウト拡散: 離散状態空間における生成拡散モデル Blackout Diffusion: Generative Diffusion Models in Discrete-State Spaces
Javier E Santos, Zachary R. Fox, Nicholas Lubbers, Yen Ting Lin
arXiv Submitted on 18 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.11089
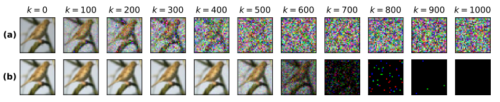
Abstract
Typical generative diffusion models rely on a Gaussian diffusion process for training the backward transformations, which can then be used to generate samples from Gaussian noise. However, real world data often takes place in discrete-state spaces, including many scientific applications. Here, we develop a theoretical formulation for arbitrary discrete-state Markov processes in the forward diffusion process using exact (as opposed to variational) analysis. We relate the theory to the existing continuous-state Gaussian diffusion as well as other approaches to discrete diffusion, and identify the corresponding reverse-time stochastic process and score function in the continuous-time setting, and the reverse-time mapping in the discrete-time setting. As an example of this framework, we introduce “Blackout Diffusion”, which learns to produce samples from an empty image instead of from noise. Numerical experiments on the CIFAR-10, Binarized MNIST, and CelebA datasets confirm the feasibility of our approach. Generalizing from specific (Gaussian) forward processes to discrete-state processes without a variational approximation sheds light on how to interpret diffusion models, which we discuss.



