2023-11-21 オークリッジ国立研究所(ORNL)
◆この成功は機械学習により3か月で達成され、新しいデータにより将来の研究に向けてモデルのトレーニングが可能となった。炭素材料の最適化と超キャパシタの応用において画期的な研究となる可能性がある。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ornl.gov/news/new-carbon-material-sets-energy-storage-record-likely-advance-supercapacitors
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-40282-1
機械学習支援による水性スーパーキャパシタ用酸素リッチ高多孔性炭素活物質の材料発見 Machine-learning-assisted material discovery of oxygen-rich highly porous carbon active materials for aqueous supercapacitors
Tao Wang,Runtong Pan,Murillo L. Martins,Jinlei Cui,Zhennan Huang,Bishnu P. Thapaliya,Chi-Linh Do-Thanh,Musen Zhou,Juntian Fan,Zhenzhen Yang,Miaofang Chi,Takeshi Kobayashi,Jianzhong Wu,Eugene Mamontov &Sheng Dai
Nature Communications Published:01 August 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40282-1
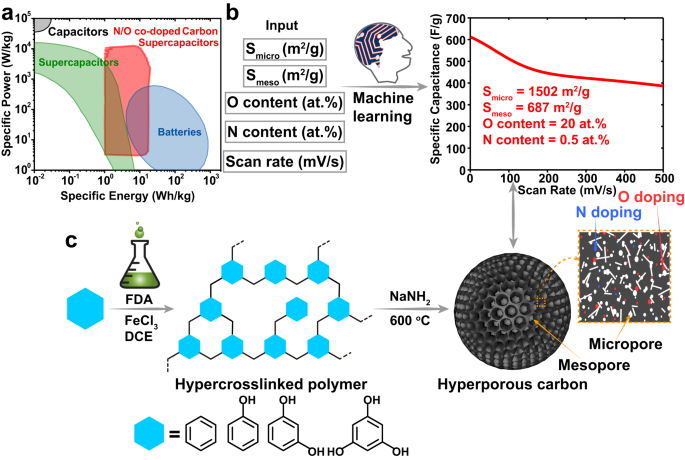
Abstract
Porous carbons are the active materials of choice for supercapacitor applications because of their power capability, long-term cycle stability, and wide operating temperatures. However, the development of carbon active materials with improved physicochemical and electrochemical properties is generally carried out via time-consuming and cost-ineffective experimental processes. In this regard, machine-learning technology provides a data-driven approach to examine previously reported research works to find the critical features for developing ideal carbon materials for supercapacitors. Here, we report the design of a machine-learning-derived activation strategy that uses sodium amide and cross-linked polymer precursors to synthesize highly porous carbons (i.e., with specific surface areas > 4000 m2/g). Tuning the pore size and oxygen content of the carbonaceous materials, we report a highly porous carbon-base electrode with 0.7 mg/cm2 of electrode mass loading that exhibits a high specific capacitance of 610 F/g in 1 M H2SO4. This result approaches the specific capacitance of a porous carbon electrode predicted by the machine learning approach. We also investigate the charge storage mechanism and electrolyte transport properties via step potential electrochemical spectroscopy and quasielastic neutron scattering measurements.



