2023-10-12 ミネソタ大学
◆この画期的な発見は、ほぼすべての日常的な電子デバイスの効率とコスト効率を向上させるために重要な結晶ナノ構造をより完璧に作成する新たな経路を提供します。
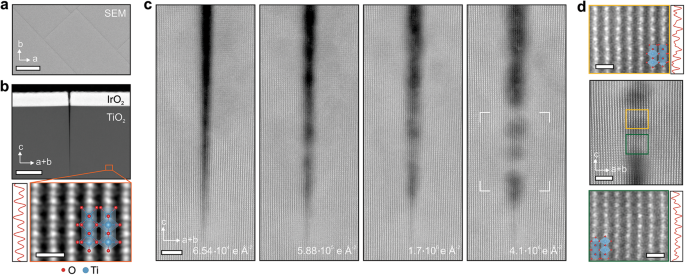
◆研究者は、電子ビームが原子ごとに新しいナノ構造を設計するために建設的に使用できることを初めて示しました。次のステップは、電子ビームの条件や結晶の温度を変えるなど、プロセスを改善または加速する方法を見つけることです。
<関連情報>
- https://cse.umn.edu/college/news/surprising-discovery-shows-electron-beam-radiation-can-repair-nanostructures
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-41781-x
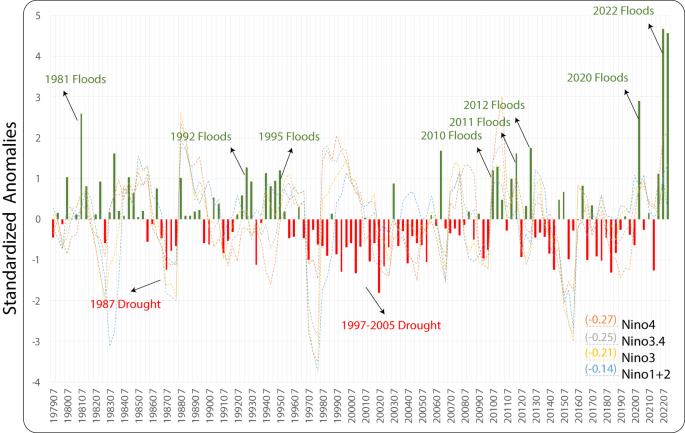
電子線ラジオリシスでルチル型酸化チタンのクラックを原子レベルで修復 Mending cracks atom-by-atom in rutile TiO2 with electron beam radiolysis
Silu Guo,Hwanhui Yun,Sreejith Nair,Bharat Jalan & K. Andre Mkhoyan
Nature Communications Published:26 September 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41781-x
Abstract
Rich electron-matter interactions fundamentally enable electron probe studies of materials such as scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). Inelastic interactions often result in structural modifications of the material, ultimately limiting the quality of electron probe measurements. However, atomistic mechanisms of inelastic-scattering-driven transformations are difficult to characterize. Here, we report direct visualization of radiolysis-driven restructuring of rutile TiO2 under electron beam irradiation. Using annular dark field imaging and electron energy-loss spectroscopy signals, STEM probes revealed the progressive filling of atomically sharp nanometer-wide cracks with striking atomic resolution detail. STEM probes of varying beam energy and precisely controlled electron dose were found to constructively restructure rutile TiO2 according to a quantified radiolytic mechanism. Based on direct experimental observation, a “two-step rolling” model of mobile octahedral building blocks enabling radiolysis-driven atomic migration is introduced. Such controlled electron beam-induced radiolytic restructuring can be used to engineer novel nanostructures atom-by-atom.