2023-06-01 ロイヤルメルボルン工科大学(RMIT)
◆この成果は、チタン合金の応用範囲を広げ、持続可能性を向上させ、革新的な合金設計を推進することに役立つ可能性があります。この発見は、航空宇宙、バイオメディカル、化学工学、宇宙、エネルギーテクノロジーなどの分野における、より持続可能な高性能タイタン合金の新たなクラスに期待を持たせています。この研究は、RMIT大学とシドニー大学を中心に行われ、香港理工大学とメルボルンのHexagon Manufacturing Intelligence社との共同研究でした。
<関連情報>
- https://www.rmit.edu.au/news/all-news/2023/jun/3d-printed-titanium-alloys
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-05952-6
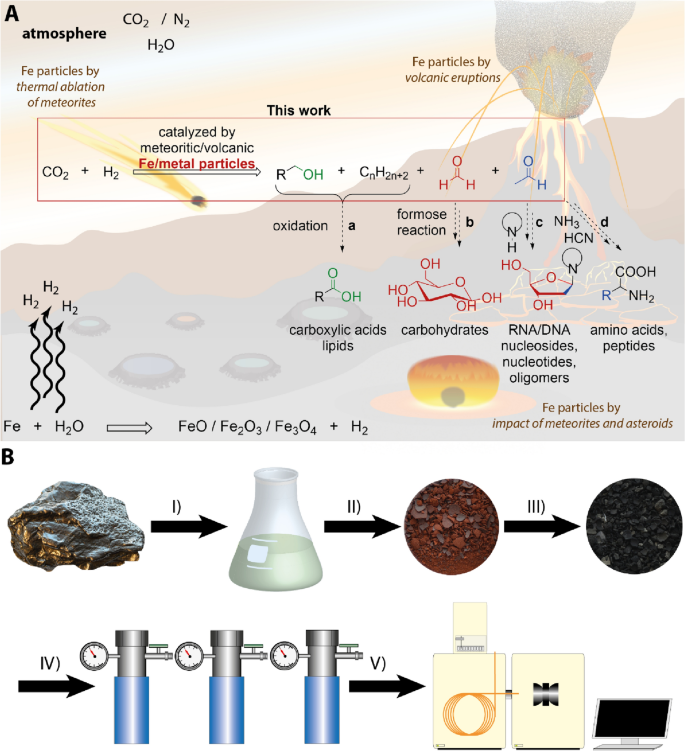
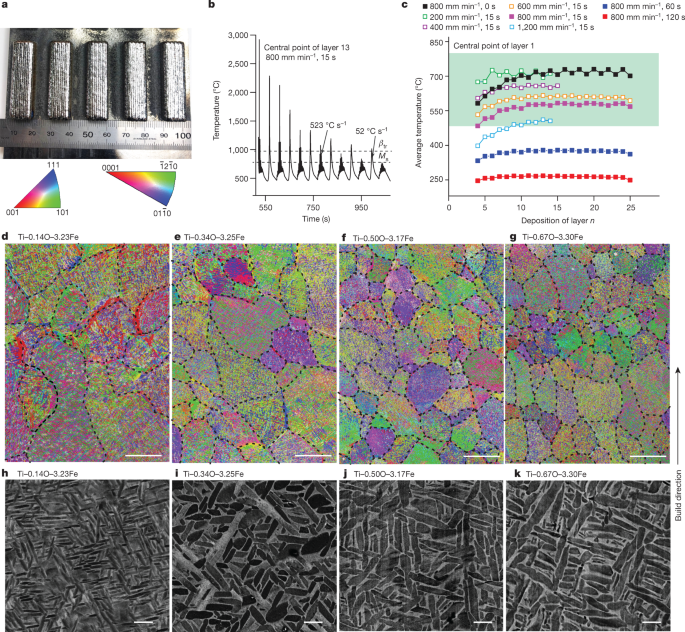
積層造形による強度と延性のあるチタン-酸素-鉄合金 Strong and ductile titanium–oxygen–iron alloys by additive manufacturing
Tingting Song,Zibin Chen,Xiangyuan Cui,Shenglu Lu,Hansheng Chen,Hao Wang,Tony Dong,Bailiang Qin,Kang Cheung Chan,Milan Brandt,Xiaozhou Liao,Simon P. Ringer & Ma Qian
Nature Published:31 May 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05952-6
Abstract
Titanium alloys are advanced lightweight materials, indispensable for many critical applications1,2. The mainstay of the titanium industry is the α–β titanium alloys, which are formulated through alloying additions that stabilize the α and β phases3,4,5. Our work focuses on harnessing two of the most powerful stabilizing elements and strengtheners for α–β titanium alloys, oxygen and iron1,2,3,4,5, which are readily abundant. However, the embrittling effect of oxygen6,7, described colloquially as ‘the kryptonite to titanium’8, and the microsegregation of iron9 have hindered their combination for the development of strong and ductile α–β titanium–oxygen–iron alloys. Here we integrate alloy design with additive manufacturing (AM) process design to demonstrate a series of titanium–oxygen–iron compositions that exhibit outstanding tensile properties. We explain the atomic-scale origins of these properties using various characterization techniques. The abundance of oxygen and iron and the process simplicity for net-shape or near-net-shape manufacturing by AM make these α–β titanium–oxygen–iron alloys attractive for a diverse range of applications. Furthermore, they offer promise for industrial-scale use of off-grade sponge titanium or sponge titanium–oxygen–iron10,11, an industrial waste product at present. The economic and environmental potential to reduce the carbon footprint of the energy-intensive sponge titanium production12 is substantial.