2023-04-06 シンガポール国立大学(NUS)
この新しい材料は、化合物で構成されている従来の強誘電体材料とは異なり、単一元素物質にも強誘電性があることを示しています。この発見は、新しい強誘電体材料の研究と設計の新しい視点を提供するだけでなく、元素材料の新しい物理学をも可能にするとされています。
今後、この新しい強誘電体材料は、量子電子デバイスや高度なデータストレージデバイスにも影響を与えると考えられています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.nus.edu.sg/novel-ferroelectric-material-for-data-storage-solutions/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-05848-5
単元素ビスマス単分子膜の2次元強誘電性 Two-dimensional ferroelectricity in a single-element bismuth monolayer
Jian Gou,Hua Bai,Xuanlin Zhang,Yu Li Huang,Sisheng Duan,A. Ariando,Shengyuan A. Yang,Lan Chen,Yunhao Lu & Andrew Thye Shen Wee
Nature Published:05 April 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05848-5
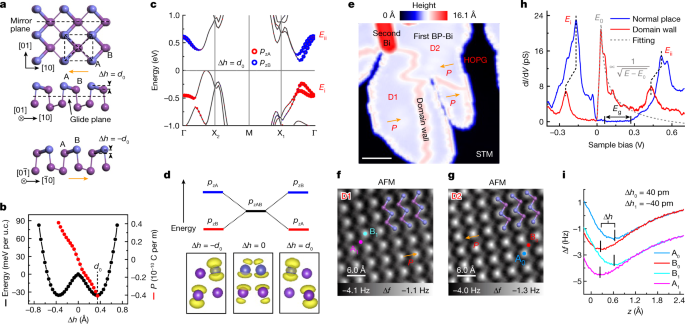
Abstract
Ferroelectric materials are fascinating for their non-volatile switchable electric polarizations induced by the spontaneous inversion-symmetry breaking. However, in all of the conventional ferroelectric compounds, at least two constituent ions are required to support the polarization switching1,2. Here, we report the observation of a single-element ferroelectric state in a black phosphorus-like bismuth layer3, in which the ordered charge transfer and the regular atom distortion between sublattices happen simultaneously. Instead of a homogenous orbital configuration that ordinarily occurs in elementary substances, we found the Bi atoms in a black phosphorous-like Bi monolayer maintain a weak and anisotropic sp orbital hybridization, giving rise to the inversion-symmetry-broken buckled structure accompanied with charge redistribution in the unit cell. As a result, the in-plane electric polarization emerges in the Bi monolayer. Using the in-plane electric field produced by scanning probe microscopy, ferroelectric switching is further visualized experimentally. Owing to the conjugative locking between the charge transfer and atom displacement, we also observe the anomalous electric potential profile at the 180° tail-to-tail domain wall induced by competition between the electronic structure and electric polarization. This emergent single-element ferroelectricity broadens the mechanism of ferroelectrics and may enrich the applications of ferroelectronics in the future.