量子と古典の世界をつなぐ新しい手法で、量子コンピュータなどの計測を改善できる可能性がある The new method bridges the quantum and classical worlds and could improve measurements in quantum computers and other applications
2022-12-21 フィンランド・アールト大学
量子の世界ではそれが可能なのです。2022年のノーベル物理学賞受賞者の一人であるアントン・ザイリンガーは、光学を用いた相互作用のない実験のアイデアを初めて実験的に実現した人物です。
今回、量子世界と古典世界のつながりを探る研究の中で、アールト大学のシュルティ・ドグラ、ジョン・J・マッコード、ゲオルゲ・ソリン・パロアヌは、相互作用のない実験を行うための新しい、より効果的な方法を発見した。研究チームは、比較的大型でありながら量子的な振る舞いを示す超伝導回路であるトランスモンデバイスを用いて、古典的な装置から発生するマイクロ波パルスの存在を検出することに成功したのだ。この研究成果は、『Nature Communications』誌に掲載された。
彼らは、トランスモンの高いエネルギーレベルを用いて、「量子性」をもう1層追加した。その結果得られる3レベルシステムの量子コヒーレンスを資源として利用した」とパラオアヌは言う。
量子コヒーレンスとは、ある物体が同時に2つの異なる状態を占めることができる可能性のことで、量子物理学が許容していることである。しかし、量子コヒーレンスは繊細で崩れやすいため、この新しいプロトコルがうまく機能するかどうかは、すぐにはわかりませんでした。ところが、この実験を最初に行ったところ、検出効率が著しく向上した。非常に低い出力のマイクロ波パルスでも効率よく検出できることも実証できました」とドグラは言う。
この実験では、量子デバイスが古典的デバイスでは不可能な結果を達成できる新しい方法も示された。これは、量子アドバンテージと呼ばれる現象である。一般に、量子的優位性を得るには、多数の量子ビットを持つ量子コンピュータが必要だと考えられているが、今回の実験では、比較的簡単な装置で本物の量子アドバンテージを実証することができた。
<関連情報>
- https://www.aalto.fi/en/news/researchers-use-quantum-mechanics-to-see-objects-without-looking-at-them
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-35049-z
超伝導回路を用いたマイクロ波パルスのコヒーレント相互作用のない検出法 Coherent interaction-free detection of microwave pulses with a superconducting circuit
Shruti Dogra,John J. McCord & Gheorghe Sorin Paraoanu
Nature Communications Published:07 December 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35049-z
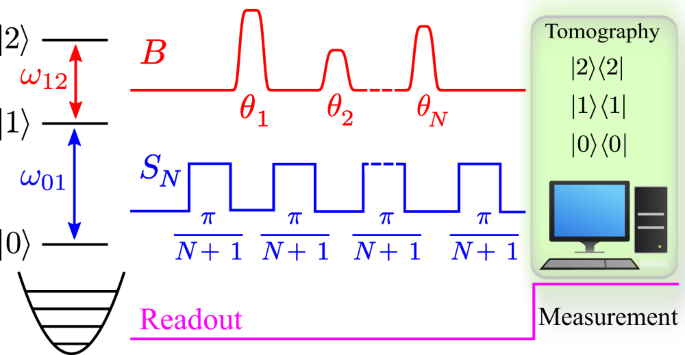
Abstract
The interaction-free measurement is a fundamental quantum effect whereby the presence of a photosensitive object is determined without irreversible photon absorption. Here we propose the concept of coherent interaction-free detection and demonstrate it experimentally using a three-level superconducting transmon circuit. In contrast to standard interaction-free measurement setups, where the dynamics involves a series of projection operations, our protocol employs a fully coherent evolution that results, surprisingly, in a higher probability of success. We show that it is possible to ascertain the presence of a microwave pulse resonant with the second transition of the transmon, while at the same time avoid exciting the device onto the third level. Experimentally, this is done by using a series of Ramsey microwave pulses coupled into the first transition and monitoring the ground-state population.