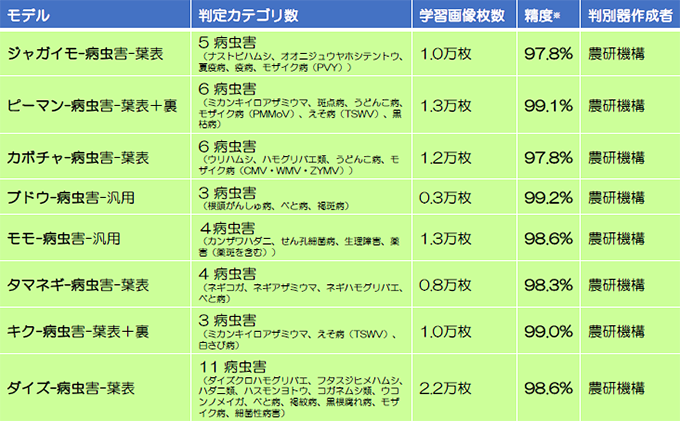
2022-01-27 アメリカ合衆国・マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
・ MIT が、2D 材料(ファンデルワールス材料)の六方晶窒化ホウ素(h-BN)による欠陥フリーの超薄膜誘電材料を利用した、微細な超伝導量子ビットを開発。
・ 従来設計の 1/100 のサイズへの量子ビットの縮小と、量子ビット同士の干渉によるクロストーク(混信)の低減を実現し、量子コンピューターの性能向上と小型量子デバイス開発を促進する。
・ 古典的コンピューターのトランジスタはナノスケールだが、量子コンピューターを構成する超伝導量子ビットはミリメートルサイズにとどまり、量子演算デバイスの小型化を阻む課題の一つとなっている。
・ 現在の量子デバイスの量子ビット数は 50~100 個だが、実用には数千~数百万個が必要となるため、量子ビットサイズの縮小と各量子ビット間の不要な混信の回避が重要。超伝導回路による量子演算プラットフォームの超伝導量子ビットには、インダクタとキャパシタが含まれる。
・ シリコン酸化物等の一般的な集積回路で使用される誘電材料は欠陥を多く含み、Q 値が約 500~1,000 と量子演算アプリケーションでは損失が過多。そのため、従来の量子キャパシタでは、上部プレートが無く下部プレートの上の真空領域が絶縁体として機能する、オープンサンドイッチ構造となっている。
・ しかし、この構造では電界を弱めてより広い層を真空領域とするためプレートサイズが拡大し、小型デバイスへの格納が不可能に。また、フリースペースの電界を持つ量子ビット同士の混信で 1 量子ビットのみの制御が難しくなるため、2 枚のプレートに欠陥フリーの誘電材料を挟んだキャパシタ構造が理想的。
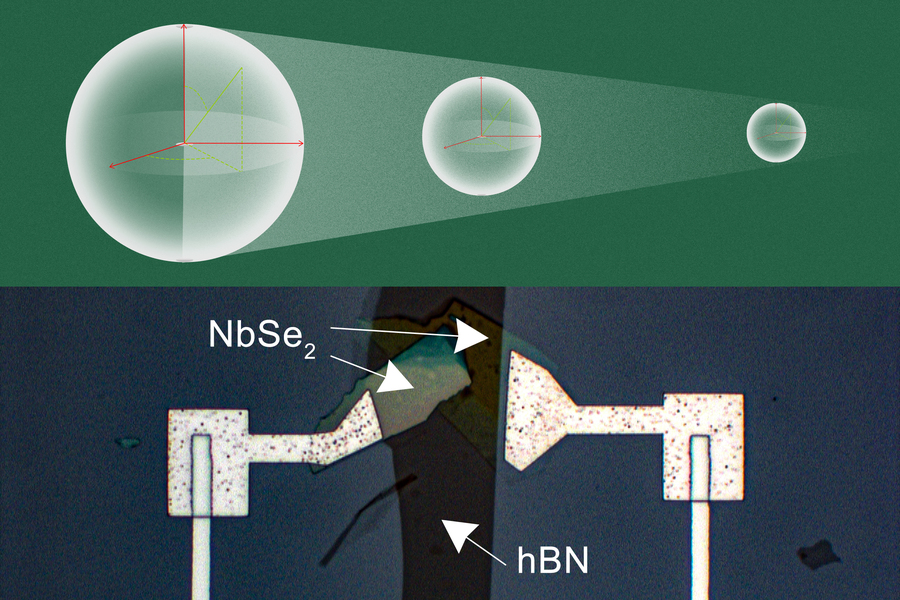
・ 本研究では、二セレン化ニオブの薄膜で h-BN 薄膜を挟み、性能損失無くフットプリントを縮減する微細なパラレルプレートキャパシタの形成を実証。同キャパシタ構造は、量子ビット間のノイズである混信を大幅に低減し、GHz 領域の高周波電界で 100,000 を超える高い Q 値を提示。
・ 今後は同手法を利用してチップ上に量子ビットを大量に作製し、混信の低減を実証する。また、同手法を改善して量子ビットの性能向上や 2D 材料のみによる量子ビットの構築を目指す。
・ 本研究は、米国陸軍研究局(ARO)、米国立科学財団(NSF)および MIT Lincoln Laboratory を通してAssistant Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering が一部資金を提供した。
URL: https://news.mit.edu/2022/tiny-materials-quibits-quantum-computing-0128
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
(関連情報)
Nature Materials 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料)
Hexagonal boron nitride as a low-loss dielectric for superconducting quantum circuits and qubits
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41563-021-01187-w
(関連情報)
Nano Letters 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料)
Miniaturizing Transmon Qubits Using van der Waals Materials
URL: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c04160
Abstract
Dielectrics with low loss at microwave frequencies are imperative for high-coherence solid-state quantum computing platforms. Here we study the dielectric loss of hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) thin films in the microwave regime by measuring the quality factor of parallel-plate capacitors (PPCs) made of NbSe2–hBN–NbSe2 heterostructures integrated into superconducting circuits. The extracted microwave loss tangent of hBN is bounded to be at most in the mid-10−6 range in the low-temperature, single-photon regime. We integrate hBN PPCs with aluminium Josephson junctions to realize transmon qubits with coherence times reaching 25 μs, consistent with the hBN loss tangent inferred from resonator measurements. The hBN PPC reduces the qubit feature size by approximately two orders of magnitude compared with conventional all-aluminium coplanar transmons. Our results establish hBN as a promising dielectric for building high-coherence quantum circuits with substantially reduced footprint and with a high energy participation that helps to reduce unwanted qubit cross-talk.