2021-10-22 アメリカ合衆国・ワシントン大学セントルイス
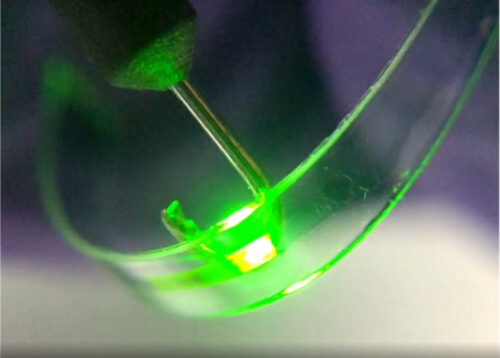
・ ワシントン大学セントルイスが、無機と有機の両種 LED の優れた特性を有する有機金属ハライドペロブスカイトベースの LED(ペロブスカイト LED: PeLED)をインクジェットプリンターで作製する新技術を開発。
・ 有機小分子やポリマー材料による有機 LED は安価でフレキシブルだが、低性能で寿命が短い。マイクロ LED 等の無機 LED は高性能・高輝度で安定しているが、高価でフレキシブル性に欠ける。
・ ポリマーバインダ製の有機ポリマーマトリクスに無機ペロブスカイト結晶を埋め込み、フレキシブルでストレッチャブルなペロブスカイト材料を作製。デバイスの性能と保護を調和させる最適な材料と最適な薄さを特定し、フレキシブルな PeLED を初めてプリント作製した。
・ PeLED の薄膜層の作製には、回転する平坦な基板にペロブスカイトを流し込むスピンコーティングが一般的に利用されるが、数千 RPM の速度で回転する基板から材料が飛び散りるため大量の材料が無駄になっている。
・ インクジェットプリンターでは、インクで紙に印刷するようにペロブスカイトを必要な場所にのみ積層するため、材料使用量を節約できる。
・ また、従来プロセスでは 5 時間を要するところ、新技術では 25 分を下回る高速作製が可能。さらに、スピンコーティングでは利用不可能なゴムをはじめ、あらゆる種類の基板へのプリントが可能に。
・ PeLED を構成するペロブスカイト層、電極層 2 枚とバッファー層の各材料層が混合しやすいため、ペロブスカイト層とその他の層の間にペロブスカイト層を保護しながら PeLED の性能への影響を抑制するポリマーを挿入してこの問題を解決した。
・ 今回開発した PeLED は、灯りをともす壁や新聞を表示するディスプレイ等を実現する、エレクトロニクス革命の最初の一歩となる。ウェアラブルデバイスやパルスオキシメーター等のスマートウェアラブルでの利用も考えられる。伸縮性のあるフレキシブルな PeLED を安価で迅速に製造できるため、思いも寄らない新技術につながる可能性も期待できる。
・ 同大学の Office of Technology Management が本技術と製造手法の特許を出願中。
URL: https://source.wustl.edu/2021/10/stretchy-bendy-flexible-leds/
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
(関連情報)
Advanced Materials 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料)
High-Speed Fabrication of All-Inkjet-Printed Organometallic Halide Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes
on Elastic Substrates
URL: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202102095
Abstract
Halide perovskites have great potential for use in high-performance light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and displays. Here, a perovskite LEDs (PeLEDs) fabricated directly on an elastomer substrate, in which every single layer in the device from bottom anode to top cathode is patterned solely using a highly scalable inkjet printing process, is reported. Compared to PeLEDs made using conventional microfabrication processes, the printing process significantly shortens the fabrication time by at least tenfold (from over 5 h to less than 25 min). The all-printed PeLEDs have a novel 4-layer structure (bottom electrode, perovskite emissive layer, buffer layer, top electrode) without separate electron or hole transporting layers. For flexible PeLEDs printed directly in ambient conditions, a turn-on voltage, maximum luminance intensity, and maximum current efficiency of 3.46 V, 10227 cd m−2, and 2.01 cd A−1, respectively, is achieved. The devices also exhibit excellent robustness and stability even when bent to a curvature radius of 2.5 mm. The reported device structure and fabrication processes can enable high-performance flexible PeLEDs to be manufactured over a larger area at extremely low cost and fast speed, which can facilitate the adoption of the promising PeLED technology in the emerging foldable displays, smart wearables, and many other applications.



