2020/6/29 パシフィック・ノースウェスト国立研究所(PNNL)
・ PNNL が、鉄を使用した金属酸化物触媒を作製する新技術を開発。
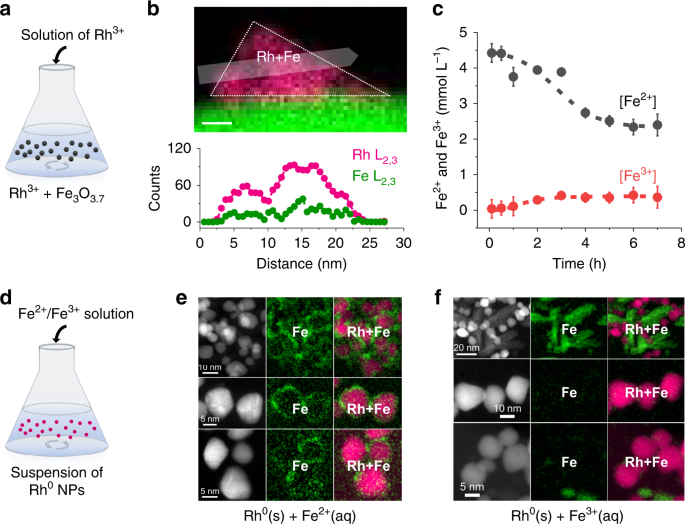
・ 同技術では、酸化鉄をコーティングしたナノ粒子を固体の酸化鉄で担持した触媒をほぼ室温下にてワンステップで作製。同触媒は、マイルドな反応条件下で CO2 を CO に還元する高活性を示す。
・ 工業用触媒の多くでは、担持構造体として酸化物のみが使用されるが、同酸化鉄ナノ粒子触媒はそれを逆転したもの。担持機能を提供しながら、合成時に表面から高反応性の鉄を放出し、金属ナノ粒子に酸化鉄のコーティングを形成する。
・ 通常このような触媒は、製造や大量生産が困難なため商業利用されていないが、技術的課題が解決できれば CO2 を産業プロセスに有用な化学物質に転換する優れたツールとして期待できる。
・ 同触媒作製技術では、酸化鉄が有する高反応性の活用により、金属酸化物担体の金属ナノ粒子に新たな特性を付与する。金属表面と組合せた酸化鉄は反応性がより高くなり、触媒反応の部位を大幅に拡大する。
・ 同触媒作製技術はまた、地表下での地化学的な金属輸送の理解にも貢献するもの。
・ 今後は、金属ナノ粒子を調整して異種の反応で利用する方法の調査と、その反応界面の化学の理解に努める。
・ 本研究は、米国エネルギー省(DOE)科学局(OST)、基礎エネルギー科学局(BES)化学・地球科学・エネルギー生物科学部および PNNL の DOE BES Geosciences プログラムが支援した。
URL: https://www.pnnl.gov/news-media/iron-chemistry-yields-surprisingly-effective-catalyst
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
(関連情報)
Nature Communications 掲載論文(フルテキスト)
Inverse iron oxide/metal catalysts from galvanic replacement
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-16830-4
Abstract
Key chemical transformations require metal and redox sites in proximity at interfaces; however, in traditional oxide-supported materials, this requirement is met only at the perimeters of metal nanoparticles. We report that galvanic replacement can produce inverse FeOx/metal nanostructures in which the concentration of oxide species adjoining metal domains is maximal. The synthesis involves reductive deposition of rhodium or platinum and oxidation of Fe2+ from magnetite (Fe3O4). We discovered a parallel dissolution and adsorption of Fe2+ onto the metal, yielding inverse FeOx-coated metal nanoparticles. This nanostructure exhibits the intrinsic activity in selective CO2 reduction that simple metal nanoparticles have only at interfaces with the support. By enabling a simple way to control the surface functionality of metal particles, our approach is not only scalable but also enables a versatile palette for catalyst design.



