(Portable electronics: a stretchable and flexible biofuel cell that runs on sweat)
2019/9/25 フランス共和国・国立科学研究センター (CNRS)

・ CNRS と米サンディエゴ大学が共同で、汗の成分を電気エネルギーに転換するフレキシブルでストレッチャブルなウェアラブル電子デバイス(「バイオ燃料電池」)を開発。
・ 特に医療や運動のモニタリングでの利用が見込まれるウェアラブル電子デバイスでは、身体に容易に統合できる安定した効率的なエネルギー供給源が必要。人間の有機的な体液に含まれる「バイオ燃料」の活用が期待されている。
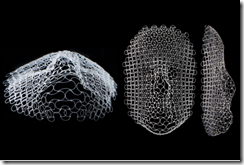
・ 同デバイスは、ストレッチャブルなコネクタで連結されたカーボンナノチューブ(CNT)、架橋ポリマーと酵素を、シルクプリンティングで直接印刷して作製。
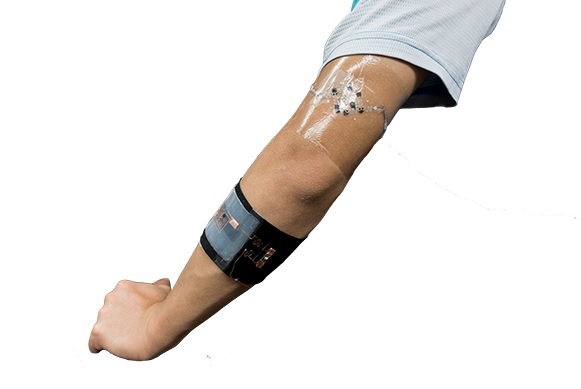
・ 皮膚に沿って変形し、酸素還元と汗に含まれる乳酸の酸化により発電。腕に装着すると電圧ブースターが継続的に LED に電力を供給。比較的シンプルで、初期コストは汗が含有する成分を変換する酵素の生成であるため、シンプル・安価に製造できる。
・ より大型のデバイスに電力を供給するために電圧を増幅する方法を探る。
URL: http://www.cnrs.fr/en/portable-electronics-stretchable-and-flexible-biofuel-cell-runs-sweat
(関連情報)
Advanced Functional Materials 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料)
Stretchable and Flexible Buckypaper‐Based Lactate Biofuel Cell for Wearable Electronics
URL: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/adfm.201905785
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
Abstract
This work demonstrates a stretchable and flexible lactate/O2 biofuel cell (BFC) using buckypaper (BP) composed of multi‐walled carbon nanotubes as the electrode material. Free‐standing BP, functionalized with a pyrene‐polynorbornene homopolymer, is fabricated as the immobilization matrix for lactate oxidase (LOx) at the anode and bilirubin oxidase at the cathode. This biofuel cell delivers an open circuit voltage of 0.74 V and a high‐power density of 520 µW cm−2. The functionalized BP electrodes are assembled onto a stretchable screen‐printed current collector with an “island–bridge” configuration, which ensures conformal contact between the wearable BFC and the human body and endows the BFC with excellent performance stability under stretching condition. When applied to the arm of the volunteer, the BFC can generate a maximum power of 450 µW. When connected with a voltage booster, the on‐body BFC is able to power a light emitting diode under both pulse discharge and continuous discharge modes during exercise. This demonstrates the promising potential of the flexible BP‐based BFC as a self‐sustained power source for next‐generation wearable electronics.