2025-12-04 清華大学
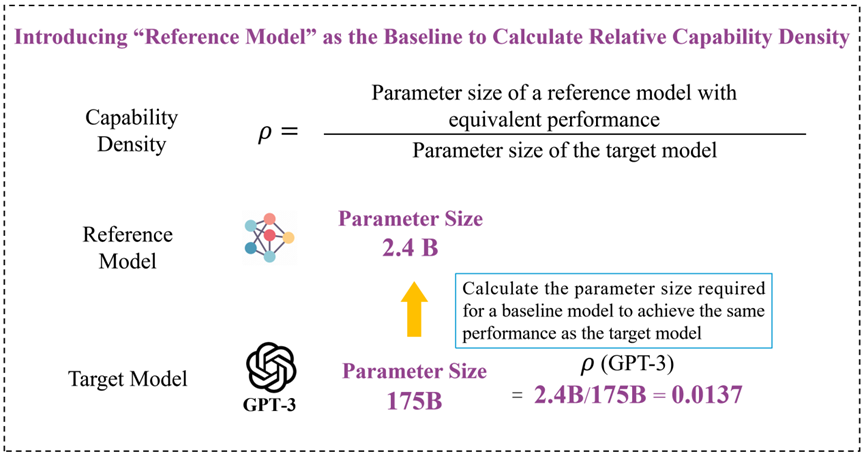 Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the calculation method for “Capability Density”
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the calculation method for “Capability Density”
<関連情報>
- https://www.tsinghua.edu.cn/en/info/1245/14611.htm
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-025-01137-0
LLMの密度法則 Densing law of LLMs
Chaojun Xiao,Jie Cai,Weilin Zhao,Biyuan Lin,Guoyang Zeng,Jie Zhou,Zhi Zheng,Xu Han,Zhiyuan Liu & Maosong Sun
Nature Machine Intelligence Published:06 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-025-01137-0
A preprint version of the article is available at arXiv.
Abstract
Large language models (LLMs) have emerged as a milestone in artificial intelligence. The scaling law indicates that the performance of LLMs can continually improve as the model size increases, which poses challenges for training and deployment. Despite numerous efforts to improve LLM efficiency, there is no general consensus on development trends and evaluation metrics for efficiency of LLMs with different scales. To address this tension between model performance and efficiency, we introduce the concept of capability density as a metric to evaluate the quality of the LLMs and describe the trend of LLMs in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency. Intuitively, capability density can be understood as the capability contained within each unit of model parameters. Capability density provides a unified framework for assessing both model performance and efficiency. Here we show an empirical observation, called the ‘densing law’, that the capability density of LLMs grows exponentially over time. More specifically, using widely used benchmarks for evaluation, the maximum capability density of open-source LLMs doubles approximately every 3.5 months. This reveals that both parameter requirements and inference costs of LLMs for achieving equivalent performance decrease exponentially, offering insights for efficient LLM development strategies.