2025-07-24 ノースウェスタン大学
<関連情報>
- https://news.northwestern.edu/stories/2025/07/sulfur-mof-fuels-catalytic-activity/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-01876-y
水素化触媒作用のための合成後改質による金属有機フレームワークへの金属-硫黄活性サイトの導入 Introducing metal–sulfur active sites in metal–organic frameworks via post-synthetic modification for hydrogenation catalysis
Haomiao Xie,Milad Ahmadi Khoshooei,Mukunda Mandal,Simon M. Vornholt,Jan Hofmann,Luke M. Tufaro,Kent O. Kirlikovali,Dawson A. Grimes,Seryeong Lee,Shengyi Su,Susanne Reischauer,Debabrata Sengupta,Kira Fahy,Kaikai Ma,Xiaoliang Wang,Fanrui Sha,Wei Gong,Yongwei Che,Jenny G. Vitillo,John S. Anderson,Justin M. Notestein,Karena W. Chapman,Laura Gagliardi & Omar K. Farha
Nature Chemistry Published:24 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-025-01876-y
Abstract
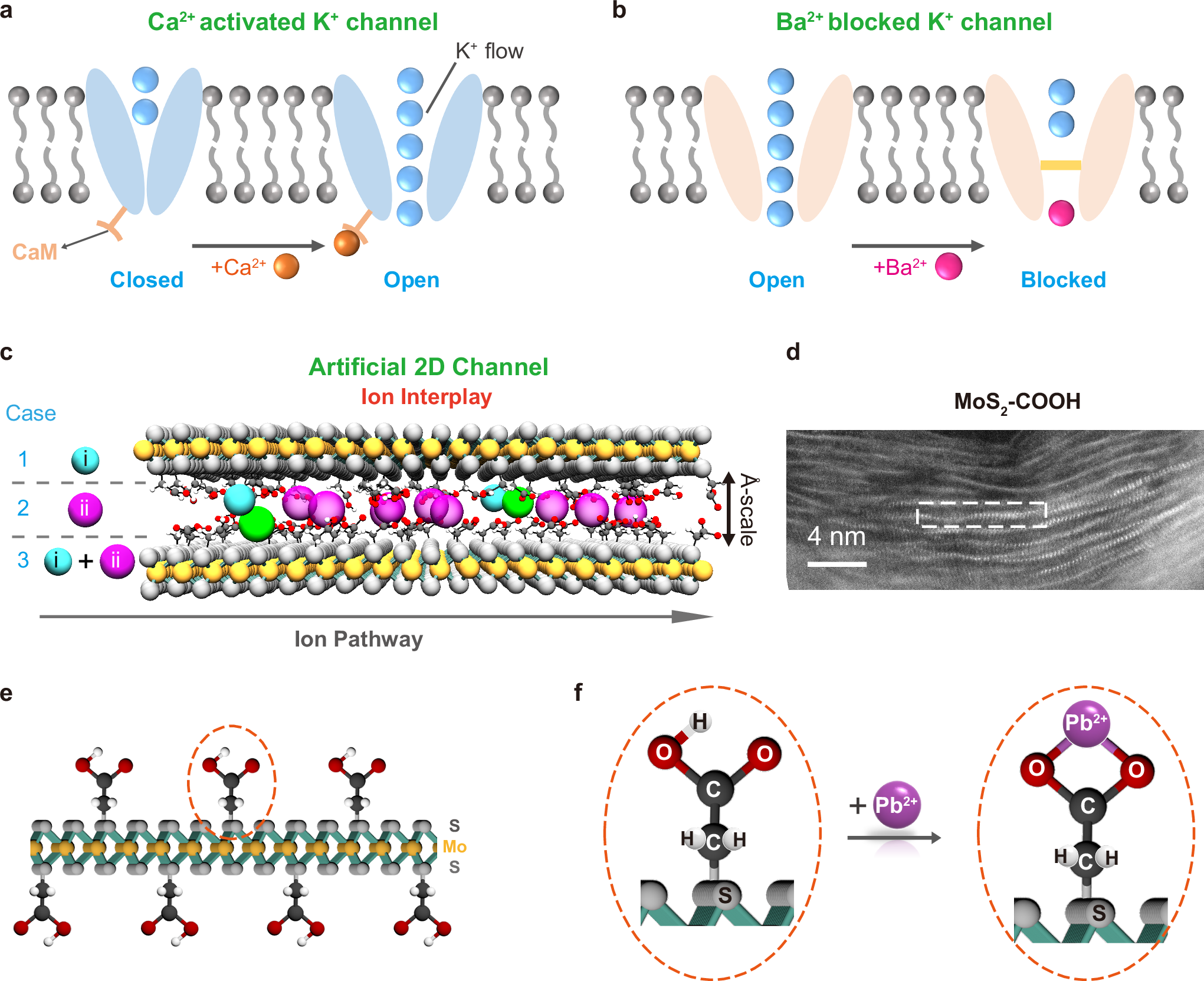
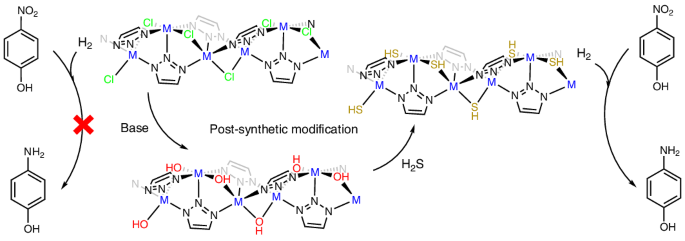
Metal–sulfur active sites play a central role in catalytic processes such as hydrogenation and dehydrogenation, yet the majority of active sites in these compounds reside on the surfaces and edges of catalyst particles, limiting overall efficiency. Here we present a strategy to embed metal–sulfur active sites into metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) by converting bridging or terminal chloride ligands into hydroxide and subsequently into sulfide groups through post-synthetic modification. We apply this method to two representative MOF families: one featuring one-dimensional metal–chloride chains and another containing discrete multinuclear metal clusters. Crystallographic and spectroscopic analyses confirm structural integrity and sulfide incorporation, and the transformation is monitored by in situ total scattering methods. The sulfided MOFs display enhanced catalytic activity in the selective hydrogenation of nitroarenes using molecular hydrogen. Density functional theory calculations indicate that sulfur incorporation promotes homolytic metal–ligand bond cleavage and facilitates H2 activation. This work establishes an approach to construct MOFs featuring accessible metal–sulfide sites.