2025-03-06 国際農研,タイ農業局
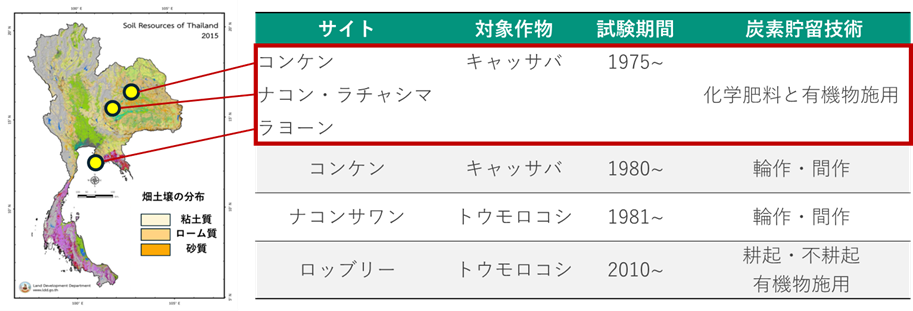
タイでの主要作物である、キャッサバ、トウモロコシを対象として、タイ国内の6地点において長期連用試験を継続しています。本研究では、赤枠内のコンケン、ナコン・ラチャシマおよびラヨーンの3地点での試験を対象としました。
<関連情報>
- https://www.jircas.go.jp/ja/release/2024/press202426
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ldr.5310
タイにおける40年以上にわたる長期圃場実験で明らかになった砂質・粘土質土壌における炭素貯留と土壌肥沃度管理 Carbon Sequestration and Soil Fertility Management in Sandy and Clayey Soils Revealed by Over Four Decades of Long-Term Field Experiments in Thailand
Somrutai Tancharoen, Shinya Iwasaki, Takeshi Watanabe, Suphakarn Luanmanee, Wanida Nobuntou, Wanlee Amonpon, Netirat Chumsuwan, Kobkiet Paisancharoen, Saowaree Bumrung, Naruo Matsumoto
Land Degradation & Development Published: 03 October 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.5310
ABSTRACT
We investigated the impact of organic matter (OM) application on soil organic carbon (SOC) sequestration and cassava yield in sandy (sand content > 72% and > 62%) and clayey (sand content > 47%) soils through three long-term experiments conducted from 1975 to 1976 in Thailand. Eight treatments—nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) fertilization, cassava residue (CR), and compost application (COM)—were assigned to the control (CT), N, NP, NK, NPK, CR, NPK + CR, and NPK + COM groups. Changes in SOC, cassava yield, and soil chemical properties, were recorded. Interactions of these parameters were visualized using structural equation modeling (SEM). SOC concentrations were determined at five different depths in 2021. A significant treatment effect was observed in the initial stage of the experiment in sandy soils. Conversely, in clayey soil, a significant effect was observed only in the later stage. SOC sequestration rates (mean ± SD of the three sites, Mg C ha−1 0.2 m−1) were in the order of NPK + COM (10.1 ± 6.5), NPK + CR (5.6 ± 3.1), CR (2.8 ± 2.0), NPK (2.0 ± 2.1), NK (1.9 ± 1.3), NP (1.8 ± 2.0), and N (1.2 ± 1.1). SEM highlighted the effect of OM application on SOC sequestration across the three sites. Furthermore, SOC increases positively influenced cassava yield in sandy but not in clayey soils. Vertical distribution of SOC showed consistent treatment effects in deeper soil layers, especially in sandy soils, underscoring the importance of considering deep soil layers for carbon sequestration.