2025-03-05 ロスアラモス国立研究所(LANL)
<関連情報>
LoRID: 逆説的純化のための低ランク反復拡散 LoRID: Low-Rank Iterative Diffusion for Adversarial Purification
Geigh Zollicoffer, Minh Vu, Ben Nebgen, Juan Castorena, Boian Alexandrov, Manish Bhattarai
arXiv Submitted on 12 Sep 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2409.08255
Abstract
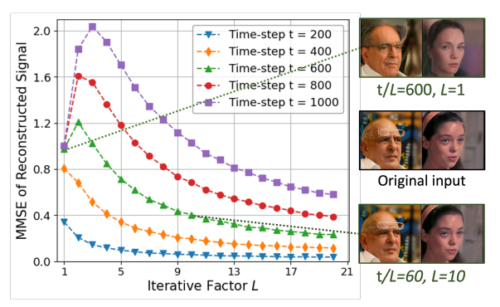
This work presents an information-theoretic examination of diffusion-based purification methods, the state-of-the-art adversarial defenses that utilize diffusion models to remove malicious perturbations in adversarial examples. By theoretically characterizing the inherent purification errors associated with the Markov-based diffusion purifications, we introduce LoRID, a novel Low-Rank Iterative Diffusion purification method designed to remove adversarial perturbation with low intrinsic purification errors. LoRID centers around a multi-stage purification process that leverages multiple rounds of diffusion-denoising loops at the early time-steps of the diffusion models, and the integration of Tucker decomposition, an extension of matrix factorization, to remove adversarial noise at high-noise regimes. Consequently, LoRID increases the effective diffusion time-steps and overcomes strong adversarial attacks, achieving superior robustness performance in CIFAR-10/100, CelebA-HQ, and ImageNet datasets under both white-box and black-box settings.