2024-10-30 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/precise-layering-in-catalysts-for-building-sustain/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41929-024-01236-y
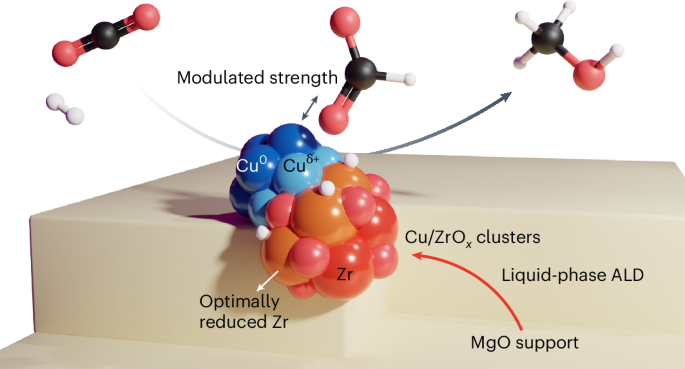
液相原子層堆積法を用いたCO2水素化用MgO上のCu/ZrOxクラスターの原子単位設計 Atom-by-atom design of Cu/ZrOx clusters on MgO for CO2 hydrogenation using liquid-phase atomic layer deposition
Seongmin Jin,Choah Kwon,Aram Bugaev,Bartu Karakurt,Yu-Cheng Lin,Louisa Savereide,Liping Zhong,Victor Boureau,Olga Safonova,Sangtae Kim & Jeremy S. Luterbacher
Nature Catalysis Published:14 October 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-024-01236-y
Abstract
The difficulty of synthesizing uniform atomically precise active sites limits our ability to engineer increasingly more active heterogeneous catalysts for the hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol. Here we design Cu/ZrOx clusters on MgO with near atomic precision for CO2 hydrogenation using a liquid-phase atomic layer deposition method. The controlled cluster structure modulates the binding strength of CO2 and moderately stabilizes monodentate formate—an essential reaction intermediate for methanol production. We achieved a methanol selectivity of 100 and 76.7% at 200 and 250 °C, respectively and a methanol productivity that was one to two orders of magnitude higher than when the same catalysts were prepared by impregnation. Ab initio computations show that Cu/ZrOx clusters can tune the oxidation of Zr, which controls the stability of reaction intermediates on the catalyst. Our approach demonstrates the potential of precise atomic control of catalytic clusters to improve catalytic productivity.