2023-03-20 カリフォルニア大学バークレー校(UCB)
Xu氏の設計手法は、人工知能に基づいており、血漿を模倣するポリマーを合成することで、人工生物学的流体を作成し、高温に対して耐性を持つことができることが証明されました。Xu氏の研究は、バイオ医薬品の分野における革命をもたらす可能性があるとされています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.berkeley.edu/2023/03/20/can-synthetic-polymers-replace-the-bodys-natural-proteins/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05675-0
タンパク質混合物を模倣する集団ベースのヘテロポリマー設計 Population-based heteropolymer design to mimic protein mixtures
Zhiyuan Ruan,Shuni Li,Alexandra Grigoropoulos,Hossein Amiri,Shayna L. Hilburg,Haotian Chen,Ivan Jayapurna,Tao Jiang,Zhaoyi Gu,Alfredo Alexander-Katz,Carlos Bustamante,Haiyan Huang & Ting Xu
Nature Published:08 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05675-0
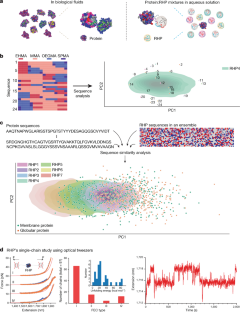
Abstract
Biological fluids, the most complex blends, have compositions that constantly vary and cannot be molecularly defined1. Despite these uncertainties, proteins fluctuate, fold, function and evolve as programmed2,3,4. We propose that in addition to the known monomeric sequence requirements, protein sequences encode multi-pair interactions at the segmental level to navigate random encounters5,6; synthetic heteropolymers capable of emulating such interactions can replicate how proteins behave in biological fluids individually and collectively. Here, we extracted the chemical characteristics and sequential arrangement along a protein chain at the segmental level from natural protein libraries and used the information to design heteropolymer ensembles as mixtures of disordered, partially folded and folded proteins. For each heteropolymer ensemble, the level of segmental similarity to that of natural proteins determines its ability to replicate many functions of biological fluids including assisting protein folding during translation, preserving the viability of fetal bovine serum without refrigeration, enhancing the thermal stability of proteins and behaving like synthetic cytosol under biologically relevant conditions. Molecular studies further translated protein sequence information at the segmental level into intermolecular interactions with a defined range, degree of diversity and temporal and spatial availability. This framework provides valuable guiding principles to synthetically realize protein properties, engineer bio/abiotic hybrid materials and, ultimately, realize matter-to-life transformations.