2026-02-18 埼玉大学
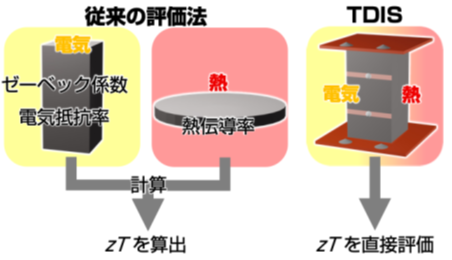
図 従来の熱電性能評価手法と、本研究で確立した時間領域インピーダンス分光法(TDIS:Time-Domain Impedance Spectroscopy)(注4)による評価手法の概念比較。従来法では、ゼーベック係数・電気抵抗率・熱伝導率を別々の測定系、場合によっては異なる試料で測定し、無次元性能指数 zT を計算によって求めていた。一方TDISでは、単一試料・単一測定系において熱と電気の応答を同時に捉えることで無次元性能指数 zT を材料の応答として直接評価できる。
<関連情報>
- https://www.saitama-u.ac.jp/topics_archives/202602181400.html
- https://www.saitama-u.ac.jp/media/pr20260218.pdf
- https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apl/article-abstract/128/7/071905/3380151/Observation-of-spatial-distribution-of?redirectedFrom=fulltext
時間領域インピーダンス分光法による 粉末焼結Bi 2 Te 3系バルク熱電材料 の無次元性能指数の空間分布の観察
Observation of spatial distribution of dimensionless figure of merit in powder-sintered Bi2Te3-based bulk thermoelectric materials via time-domain impedance spectroscopy
Hitoyuki Sato;Yasuhiro Hasegawa
Applied Physics Letters Published:February 17 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0313465
The time-domain impedance spectroscopy (TDIS) method enables direct determination of the dimensionless figure of merit (zT) from a single thermoelectric specimen, eliminating uncertainties associated with sample-to-sample variations inherent in conventional measurements. This work demonstrates direct, spatially resolved zT measurements within a powder-sintered bulk ruthenium-doped Bi2Te3 specimen, allowing quantitative mapping of its spatial distribution. Three 3 × 3 × 5 mm3 specimens, equipped with thin-film Ti/Cu electrodes, were randomly selected from the same bulk. Impedance and transient-resistance responses were measured at 300 K under high-vacuum and temperature-stabilized conditions. The TDIS method achieved a zT uncertainty below 1.5% and quantitatively resolved spatial variations ranging from 0.413 ± 0.005 to 0.475 ± 0.007 over a distance of 5 mm, providing experimental evidence that intrinsic transport-defined zT inhomogeneity is manifested as spatial zT variations in powder-sintered bulk materials. Distinct local variations in thermoelectric properties (zT and resistivity) were detected even within nominally homogeneous powder-sintered bulk materials. Electrode geometry also affected the observed distribution, with point electrodes exhibiting larger fluctuations (approximately 7%) than strip electrodes (<3%). These results demonstrate the presence of measurable spatial zT variation within a single specimen and highlight the importance of accounting for material inhomogeneity when evaluating thermoelectric performance.