2025-11-16 中国科学院(CAS)
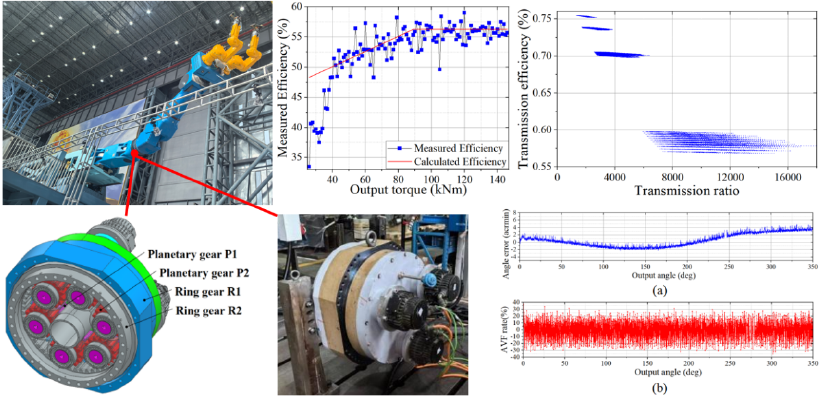 Heavy-duty robotic arm joint and parameter optimization (Image by CHENG Yong)
Heavy-duty robotic arm joint and parameter optimization (Image by CHENG Yong)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/phys/202511/t20251124_1133133.shtml
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0952197625018998
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0952197625013090
実践学習による融合アプリケーションにおける自律アセンブリの習得:ペグインホール研究 Mastering autonomous assembly in fusion application with learning-by-doing: A peg-in-hole study
Ruochen Yin, Huapeng Wu, Ming Li, Yong Cheng, Yuntao Song, Hongtao Pan, Heikki Handroos
Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence Available online: 8 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2025.111897
Abstract
Robotic peg-in-hole assembly represents a critical area of investigation in robotic automation. Traditional approaches primarily rely on optical or force/torque (F/T) sensors, each with inherent limitations: restricted assembly accuracy or inefficient peg-hole alignment. Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) based methods have the potential to combine data from both types of sensors to achieve improved results. However, our application scenario is situated inside a fusion reactor, where the radiation environment and the abundance of smooth metal surfaces make commonly used three-dimensional (3D) sensors face operational challenges. To address this, we propose a novel DRL-based approach that, unlike conventional methods, integrates data from a two-dimensional (2D) camera and an F/T sensor. This approach trains the agent to perform peg-in-hole assembly tasks by mimicking human hand-eye coordination. It utilizes multi-input branch neural network to fuse multi-sensor data with significant differences and automatically adjusts the weights of multi-source data at different stages of assembly, thereby simultaneously meeting the requirements of fast alignment and high-precision assembly. Real-world experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of this multi-sensor fusion approach, particularly in rigid peg-in-hole assembly tasks. It achieves rapid assembly with a peg-hole clearance of less than 0.1 mm (smaller than the repeatable accuracy of the robotic arm we used) while maintaining a high success rate and avoiding risky behaviors. This study shows that high-precision peg-in-hole assembly operations can be successfully accomplished using only a 2D camera as the optical sensor. This advancement significantly contributes to the development of high-precision automated operations in challenging environments, such as radiation-exposed settings.
トランスフォーマーベースのクロスタスクインタラクションによるプリミティブセグメンテーションの強化 Enhancing primitive segmentation through transformer-based cross-task interaction
Tao Wang, Weibin Xi, Yong Cheng , Jun Zhang, Ruochen Yin, Yang Yang
Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence Available online: 13 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2025.111307
Abstract
Point cloud primitive segmentation, which divides a point cloud into surface patches of distinct primitive types, is fundamental to three-dimensional objects processing and recognition. However, existing deep learning methods for primitive segmentation lack the capability to capture global spatial relationships across tasks, limiting the exploitation of inter-task consistency. To address this issue, we propose a novel transformer-based cross-task interaction primitive segmentation (TCIPS) method that models global spatial relationships between all tasks, leading to improved segmentation accuracy. Specifically, TCIPS leverages center offset and regional purity prediction as auxiliary tasks, providing supplementary supervision to facilitate the learning of spatial and boundary information, thereby promoting richer and more generalized feature learning. Furthermore, we design a cross-task transformer fusion module that fuses and refines features from task-specific decoders using two types of transformer blocks: the feature fusion block and the task query block. Extensive experiments and comparisons with state-of-the-art methods demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our approach. Codes and models are publicly available at https://github.com/MingFengHill/TCIPS.