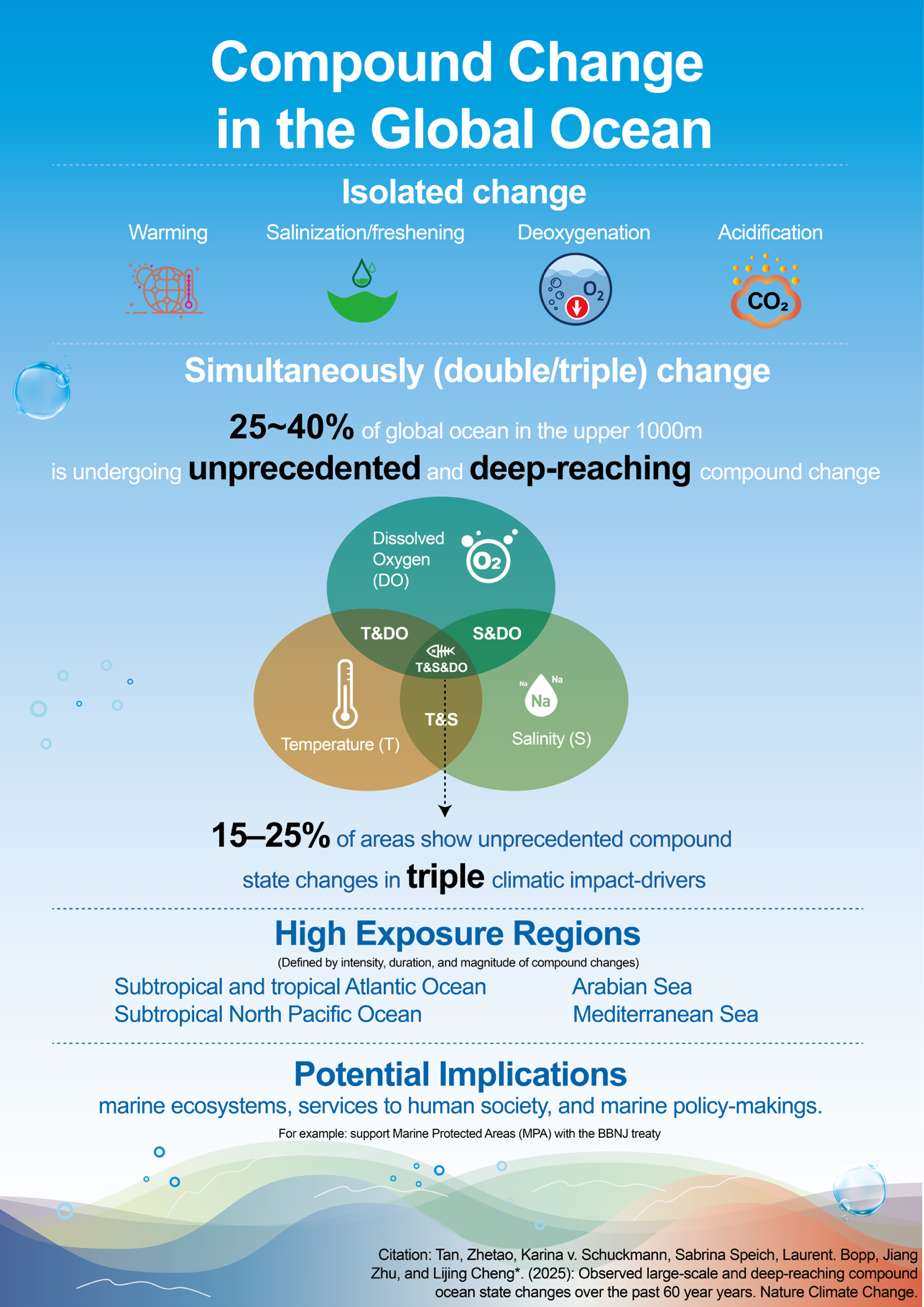
2025-11-26 東京科学大学
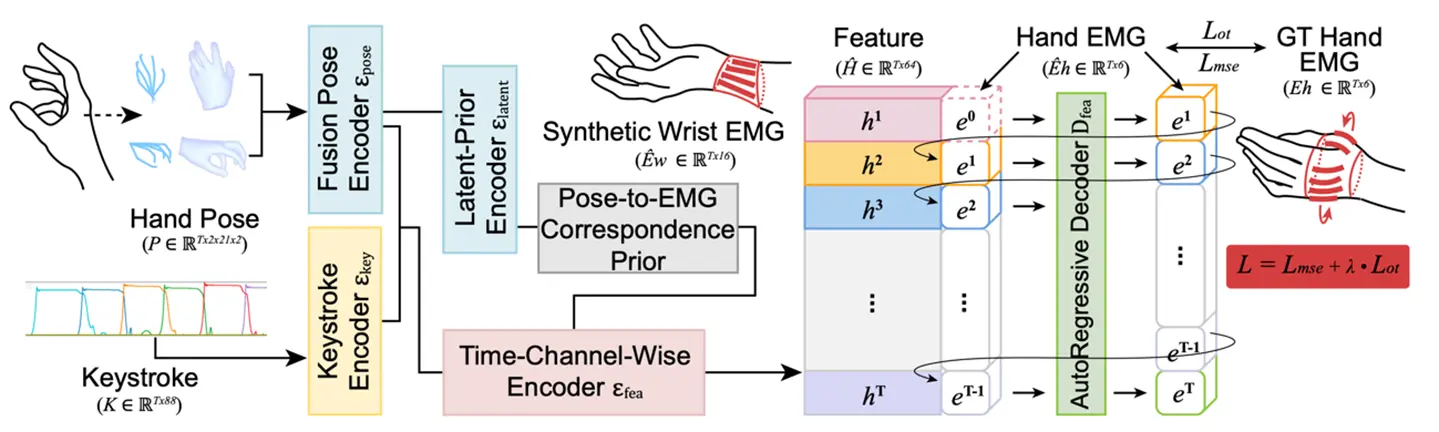
図1. 筋電推定ネットワークPianoKMP Netのアーキテクチャ
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/hoaca0bklrip
- https://neurips.cc/virtual/2025/loc/san-diego/poster/116792
ポーズから筋肉へ:ピアノの手の筋肉の筋電図のためのマルチモーダル学習 From Pose to Muscle: Multimodal Learning for Piano Hand Muscle Electromyography
Ruofan Liu, Yichen Peng, Takanori Oku, Chen-Chieh Liao, Erwin Wu, Shinichi Furuya, Hideki Koike
Proc. On 39th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2025)
Abstract
Muscle coordination is fundamental when humans interact with the world. Reliable estimation of hand muscle engagement can serve as a source of internal feedback, supporting the development of embodied intelligence and the acquisition of dexterous skills. However, contemporary electromyography (EMG) sensing techniques either require prohibitively expensive devices or are constrained to gross motor movements, which inherently involve large muscles. On the other hand, EMGs exhibit dependency on individual anatomical variability and task-specific contexts, resulting in limited generalization. In this work, we preliminarily investigate the latent pose-EMG correspondence using a general EMG gesture dataset. We further introduce a multimodal dataset, PianoKPM Dataset, and a hand muscle estimation framework, PianoKPM Net, to facilitate high-fidelity EMG inference. Subsequently, our approach is compared against reproducible competitive baselines. The generalization and adaptation across unseen users and tasks are evaluated by quantifying the training set scale and the included data amount.