2025-09-02 中国科学院(CAS)
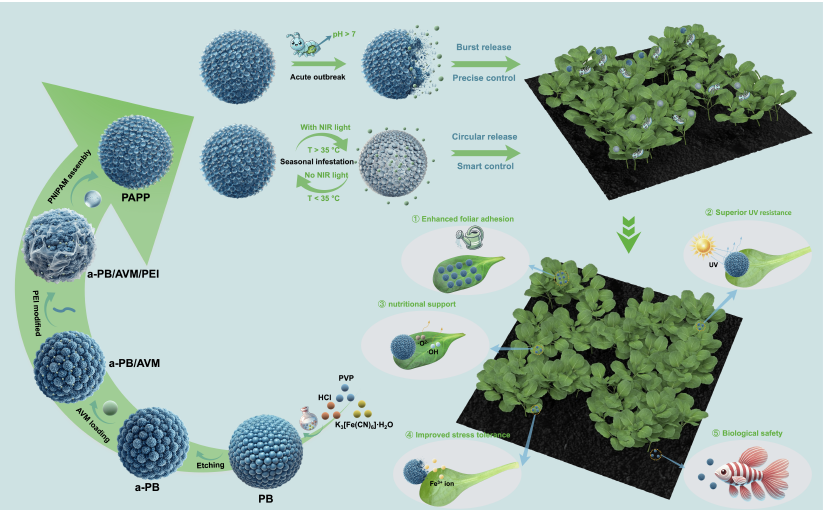
Schematic illustration of fabrication and mechanism of bioinspired Prussian blue nanopesticides. (Image by TENG Guopeng)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/phys/202511/t20251118_1116522.shtml
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0168365925007746
生態適応型害虫管理のための三刺激応答ゲートを備えたバイオインスパイアードプルシアンブルーナノ農薬 Bioinspired prussian blue nanopesticides with triple-stimuli-responsive gates for ecology-adaptive pest management
Guopeng Teng, Biao Hong, Xueqi Ma, Dongdong Li, Xue Yuan, Bowen Shen, Huan Xu, Jia Zhang, Zhengyan Wu, Chaowen Chen
Journal of Controlled Release Available online: 24 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.114162
Highlights
- Alkaline-triggered burst release controls acute pest, while thermal/NIR-responsive enables sustained seasonal efficacy.
- Nanopesticides exhibit notable UV resistance and outstanding foliar adhesion, ensuring prolonged field stability.
- Ecological assessments reveal minimal non-target effects and added Fe nutrient benefits from nanoparticle degradation.
Abstract
The escalating complexity of pest dynamics, characterized by intensifying seasonal pressures and unpredictable acute outbreaks, necessitates advanced agrochemicals capable of dynamically adapting to ecological rhythms. Inspired by the dual-phase biocontrol strategy of parasitoid wasps (immediate paralysis and sustained suppression), we engineered a Prussian blue (PB)-based nanopesticide (PAPP) with spatiotemporally decoupled release modes. Architecturally, the system integrates pH-responsive PB (alkaline-triggered disintegration) cores with thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM, heat-induced volumetric transition) nanohydrogel gates, achieving dual-modal pest management: alkaline-triggered burst avermectin (AVM) release (91.1 % discharge) for acute infestations, and temperature/NIR-programmed sustained release for seasonal maintenance. Notably, the PAPP demonstrates high drug-loading capacity (82 mg/g), along with enhanced field resilience, including improved UV resistance (67.7 % retention improvement) and significantly superior foliar adhesion (330 % increment). Physicochemical characterizations combined with molecular dynamics simulations confirm its stability and efficiency. In situ bioassays validate an 81.7 % mortality rate of Plutella xylostella, while simultaneously maintaining crop tolerance against oxidative stress and minimizing adverse effects on non-target organisms such as zebrafish and plants. Crucially, Fe ions from PB degradation supplement micronutrient uptake. This work establishes a paradigm for ecological precision agriculture through pest-behavior-driven material programming.



