2025-10-22 北海道大学
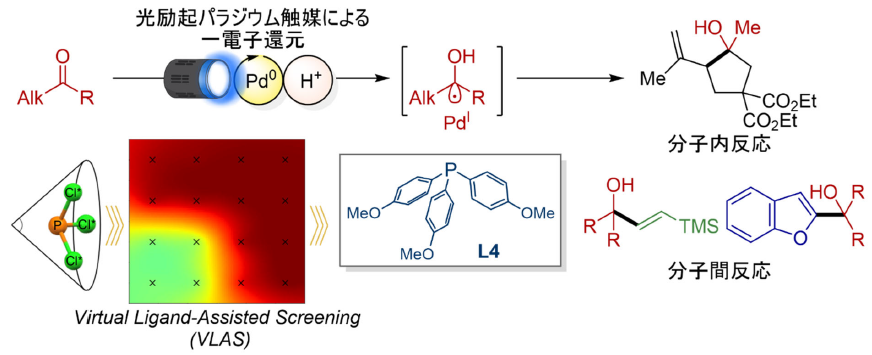
VLAS法を活用した光励起パラジウム触媒を用いたアルキルケトンからのケチルラジカル生成
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/2025/10/virtual-ligand-assisted-screeningvlas.html
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/251022_pr.pdf
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.5c13115
光励起パラジウム触媒を用いたアルキルケトンからのケチルラジカル生成のための仮想リガンド支援スクリーニング Virtual Ligand-Assisted Screening for the Generation of Ketyl Radicals from Alkyl Ketones via Photoexcited Palladium Catalysis
Kosaku Tanaka III,Ren Yamada,Suvankar Debbarma,Wataru Kanna,Hiroki Hayashi,Wataru Matsuoka,Satoshi Maeda,and Tsuyoshi Mita
Journal of the American Chemical Society Published: October 20, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c13115
Abstract
Ketyl radicals are versatile radical intermediates that enable diverse C–C-bond-forming reactions. However, their generation from substrates with highly negative potentials such as alkyl ketones via single-electron reduction remains underdeveloped. In this study, we report a new strategy that harnesses the strong reducing power of photoexcited palladium species to provide access to ketyl radicals from alkyl ketones and to promote subsequent C–C-bond-forming reactions. The key to this approach is a computationally guided virtual ligand-assisted screening (VLAS) strategy. Mechanistic investigations revealed that back-electron transfer (BET) is the major factor suppressing reactivity. By systematically evaluating virtual phosphine ligands with varying electronic and steric properties, we established design guidelines for ligands that effectively suppress BET and promote the desired transformations. Using the optimized ligands identified through VLAS, we developed efficient reductive couplings and Heck-type reactions involving both unactivated alkenes and alkynes, which are challenging substrates under conventional SmI2-mediated conditions. This work highlights a powerful paradigm that integrates photoexcited transition-metal catalysis with in-silico ligand design, enabling control over single-electron-transfer processes and opening new avenues for radical-based synthetic transformations.