2025-09-04 国立再生可能エネルギー研究所(NREL)
NRELはBlue Frontier社と共同で、冷房・除湿・蓄エネルギーを一体化した空調システム「ESEAC」を開発した。従来の圧縮式冷却と加熱による除湿を同時に行う方式は非効率だったが、ESEACは液体デシカントでの除湿と高効率の間接蒸発冷却を分離し、大幅な省エネを実現する。これにより冷房電力消費を45%以上削減し、需要ピーク時の電力使用を90%超抑制できる。さらに、内蔵の蓄エネルギー機能により電力料金の高い時間帯の負荷を回避し、建物の運用コストを下げると同時に電力グリッドの安定化に寄与する。再生可能エネルギーと組み合わせた活用も想定され、建物のエネルギー管理や需要ピークシフトを支える技術として注目される。
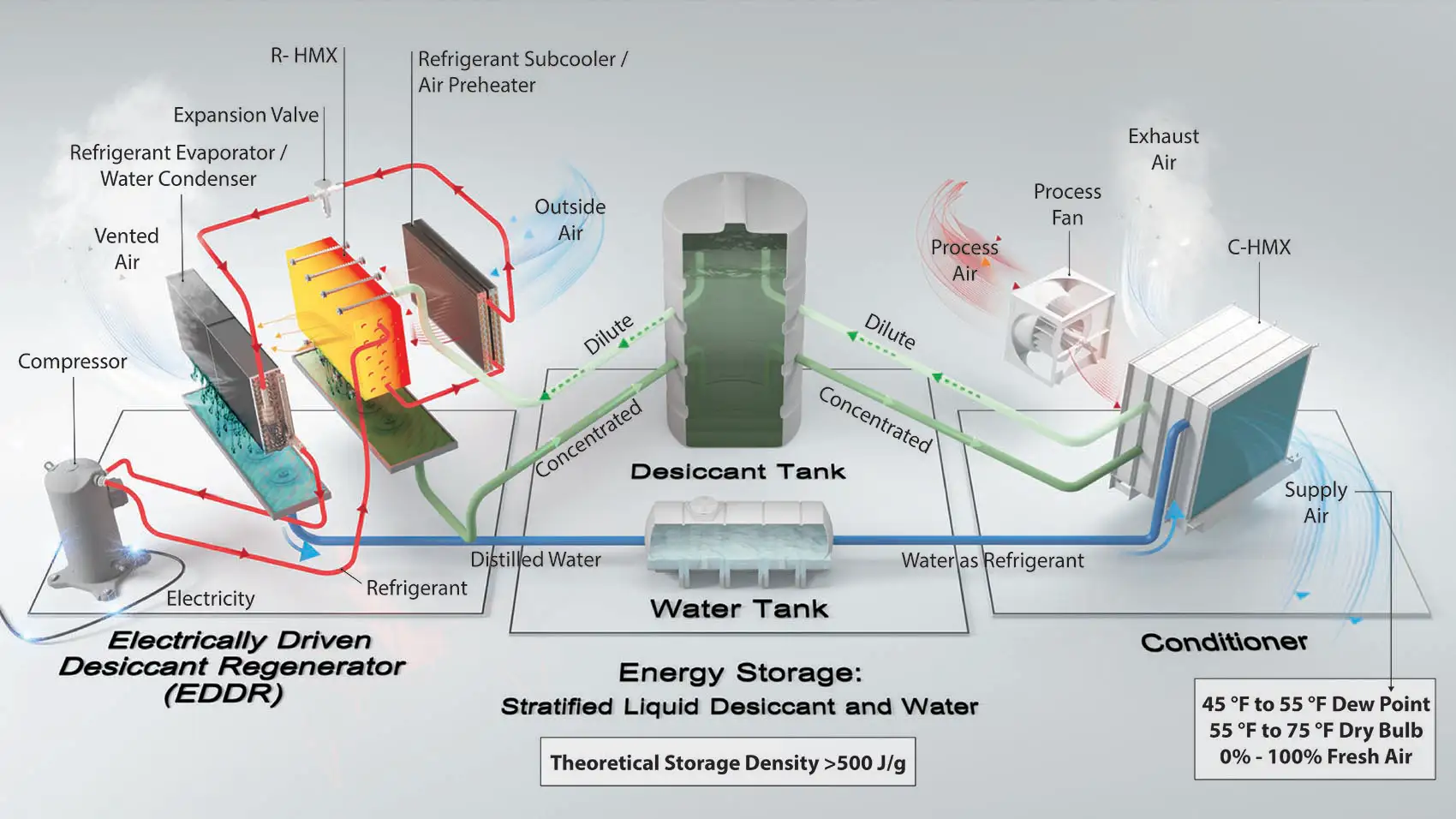
The ESEAC system comprises three innovative sub-systems that together create an all-new air conditioning system: 1) The Electrically Driven Desiccant Regenerator uses >90% of the system’s electricity to separate a diluted desiccant solution into distilled water and concentrated liquid desiccant. 2) The Energy Storage tanks hold the separated fluids for later use. 3) The Conditioner dries and cools the air by using the stored concentrated liquid desiccant and distilled water, requiring minimal electricity to operate pumps and fans. The conditioner then absorbs moisture from the air and returns diluted desiccant solution to the storage tanks. Graphic by Joshua Bauer, NREL
<関連情報>