2025-09-02 産業技術総合研究所
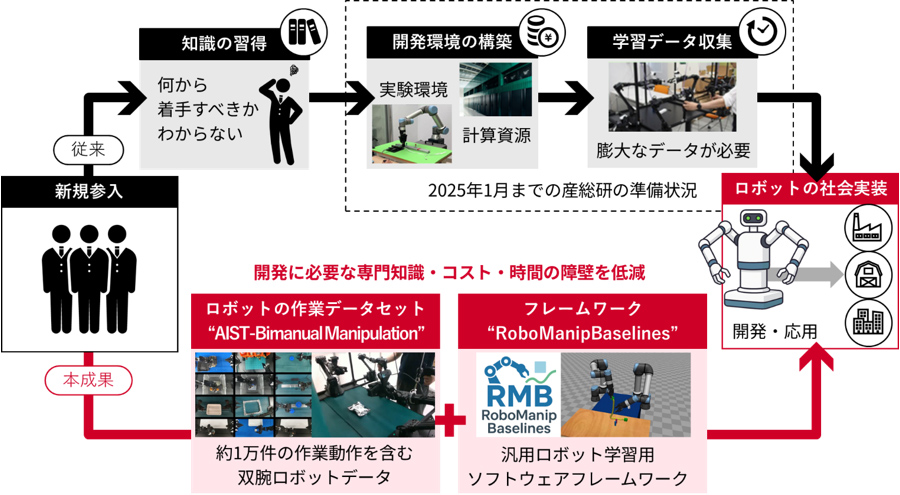
ロボット基盤モデルの開発を促進するオープンデータソース・フレームワークに関する概要
※ウェブサイト(https://github.com/isri-aist/RoboManipBaselines)の図を引用・改変したものを使用しています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.aist.go.jp/aist_j/press_release/pr2025/pr20250902/pr20250902.html
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.13916
トランスフォーマーを用いた動作チャンキングと両腕協調による両手操作学習 Learning Bimanual Manipulation via Action Chunking and Inter-Arm Coordination with Transformers
Tomohiro Motoda, Ryo Hanai, Ryoichi Nakajo, Masaki Murooka, Floris Erich, Yukiyasu Domae
arXiv Submitted on 18 Mar 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2503.13916
Abstract
Robots that can operate autonomously in a human living environment are necessary to have the ability to handle various tasks flexibly. One crucial element is coordinated bimanual movements that enable functions that are difficult to perform with one hand alone. In recent years, learning-based models that focus on the possibilities of bimanual movements have been proposed. However, the high degree of freedom of the robot makes it challenging to reason about control, and the left and right robot arms need to adjust their actions depending on the situation, making it difficult to realize more dexterous tasks. To address the issue, we focus on coordination and efficiency between both arms, particularly for synchronized actions. Therefore, we propose a novel imitation learning architecture that predicts cooperative actions. We differentiate the architecture for both arms and add an intermediate encoder layer, Inter-Arm Coordinated transformer Encoder (IACE), that facilitates synchronization and temporal alignment to ensure smooth and coordinated actions. To verify the effectiveness of our architectures, we perform distinctive bimanual tasks. The experimental results showed that our model demonstrated a high success rate for comparison and suggested a suitable architecture for the policy learning of bimanual manipulation.